In engineering, fabrication, and industrial applications, density is a critical property that directly impacts design and functionality. Among the various grades of stainless steel, 304 stainless steel stands out for its versatility, strength, and corrosion resistance. This article explores the density of 304 stainless steel, its significance, and its applications across industries, shedding light on why this property is essential for engineers and designers.
Introduction to 304 Stainless Steel
Austenitic 304 stainless steel is one of the most widely used grades due to its excellent mechanical properties, manufacturability, and resistance to corrosion. Its chemical composition, including approximately 18-20% chromium and 8-10.5% nickel, provides robust protection against environmental degradation. This makes it ideal for industries requiring lightweight yet durable materials, such as food processing, chemical manufacturing, and construction.
Definition and Composition
304 stainless steel is an austenitic alloy primarily composed of iron, with significant amounts of chromium (18-20%) and nickel (8-10.5%), along with smaller quantities of other elements. These components contribute to its key characteristics:
- Corrosion Resistance: Chromium forms a protective oxide layer, shielding the material from rust and corrosion, even in harsh environments.
- Durability: Nickel enhances toughness, making it suitable for dynamic applications.
- Low Carbon Content: Limited to 0.08%, ensuring excellent weldability and post-weld performance.
- Additional Elements: Manganese, silicon, and carbon improve mechanical properties and ease of fabrication.
These properties make 304 stainless steel a preferred choice for applications requiring hygiene and durability, such as food processing equipment and chemical storage tanks.
Key Characteristics
304 stainless steel is renowned for its unique combination of properties, making it suitable for diverse applications:
- Corrosion Resistance: High chromium and nickel content (18-20% and 8-10.5%, respectively) provide excellent resistance to rust and low-acidity environments.
- Thermal Resistance: Resists scaling at temperatures up to 870°C (1600°F), maintaining structural integrity in high-heat applications.
- Non-Magnetic: In its annealed state, it is non-magnetic, ideal for sensitive applications.
- Fabrication Ease: Easy to weld and machine, supporting complex designs in construction and manufacturing.
Importance of Density in Stainless Steel
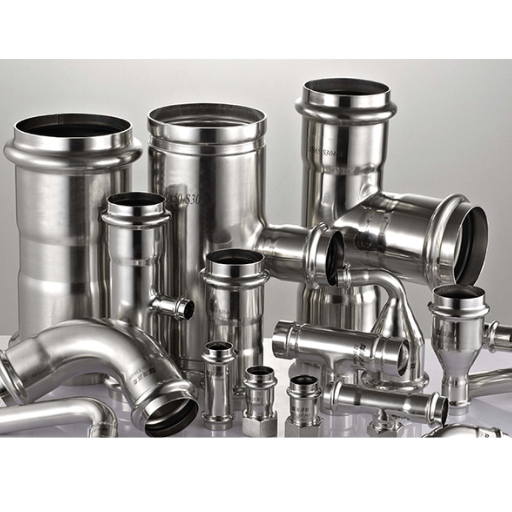

Density, a measure of mass per unit volume, is a critical property for stainless steel, typically ranging between 7.5 and 8.0 g/cm³ for 304 stainless steel, depending on alloy composition. This density strikes a balance between strength and weight, making it suitable for applications where structural stability and load distribution are key.
- Construction: Density supports structural stability without adding excessive weight.
- Transportation: Lower density contributes to fuel efficiency in automotive and aerospace applications.
- High-Tech Applications: Used in robotics and medical implants for its optimal density-to-strength ratio.
Recent trends, as observed in online search data, highlight growing interest in lightweight materials like 304 stainless steel for innovative applications, emphasizing performance and cost efficiency.
Density of 304 Stainless Steel
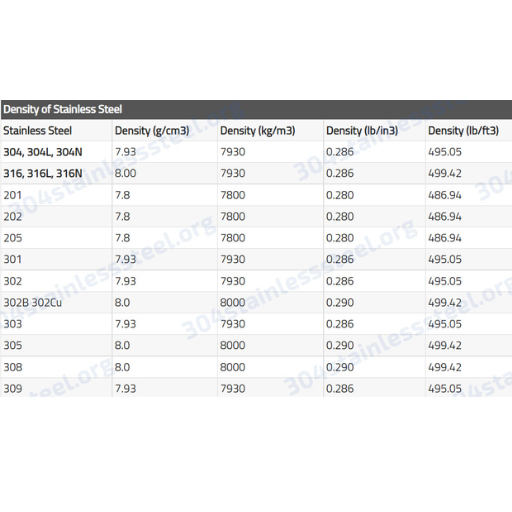
The density of 304 stainless steel is approximately 8.0 g/cm³ (8000 kg/m³) at room temperature. This value is consistent across standard conditions and is influenced by the alloy’s composition, primarily iron, chromium, and nickel.
Factors Influencing Density
Several factors can cause slight variations in the density of 304 stainless steel:
- Alloy Composition: Variations in chromium, nickel, or other elements can marginally affect density.
- Manufacturing Processes: Techniques like casting, forging, or cold working may introduce minor density changes.
- Temperature and Pressure: Extreme conditions can influence density, though changes are minimal in standard applications.
- Impurities: Production-related impurities may cause slight deviations within acceptable tolerances.
Typical Density Values
The table below summarizes the density of 304 stainless steel compared to other materials:
| Material | Density (g/cm³) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| 304 Stainless Steel | 8.0 | Standard value at room temperature |
| 316 Stainless Steel | 8.0 | Similar density, higher corrosion resistance due to molybdenum |
| Low Carbon Steel | 7.85 | Slightly lower density, less corrosion resistance |
Mechanical Properties of 304 Stainless Steel
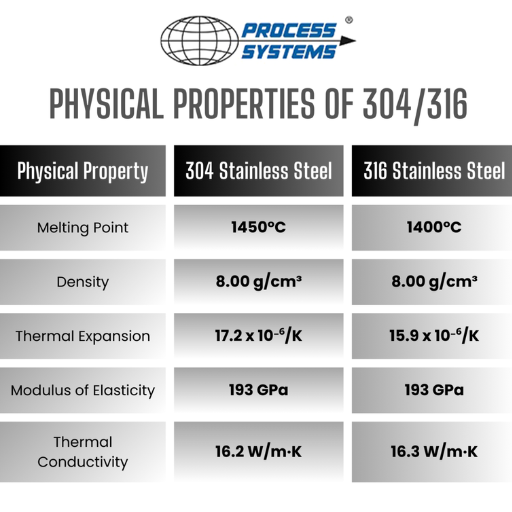
304 stainless steel offers impressive mechanical properties, making it a reliable choice for demanding applications:
- Tensile Strength: 515–750 MPa, depending on conditions.
- Yield Strength: Approximately 540 MPa.
- Elongation: Up to 40% at break, indicating high ductility.
- Hardness: Brinell hardness of 201, providing resistance to wear.
- Temperature Performance: Maintains properties in both high and low temperatures.
Strength and Durability
The combination of high yield strength and corrosion resistance ensures 304 stainless steel performs well under mechanical stress and harsh environments, making it ideal for long-term applications.
Corrosion Resistance
The high chromium (18-20%) and nickel (8-10.5%) content forms a self-repairing oxide layer, protecting against rust and corrosion, even in water or acidic environments. However, for chloride-heavy settings like seawater, 316 stainless steel is recommended due to its molybdenum content.
Comparison with Other Stainless Steel Grades
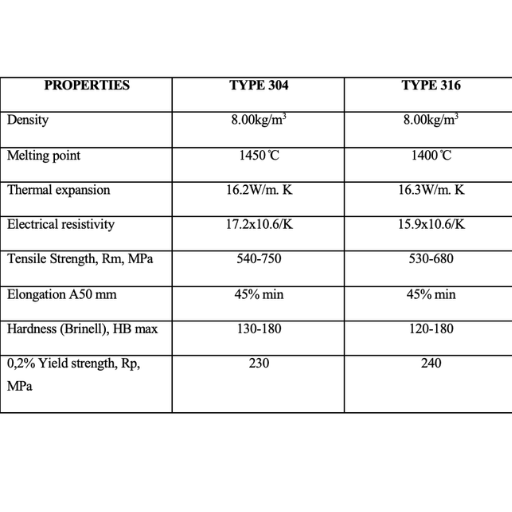
The table below compares 304 stainless steel with other grades:
| Grade | Key Features | Applications |
|---|---|---|
| 304 | High corrosion resistance, cost-effective, hygienic | Food processing, kitchen equipment, construction |
| 316 | Enhanced corrosion resistance with 2-3% molybdenum | Marine, chemical, and coastal applications |
| 430 | Lower cost, reduced corrosion resistance | Decorative applications, appliances |
| 410 | High hardness, wear resistance | Tools, equipment |
Applications of 304 Stainless Steel
304 stainless steel is used across various industries due to its versatility and performance:
- Kitchen Equipment: Sinks, cutlery, and appliances for their resistance to food acids and ease of cleaning.
- Food and Beverage: Processing tanks and equipment due to hygiene and corrosion resistance.
- Architecture: Building facades and railings for durability and aesthetic appeal.
- Medical: Surgical instruments and hospital furniture for sterilizability.
- Automotive: Trim and exhaust systems for corrosion resistance and durability.
Advantages of 304 Stainless Steel
- Chemical Resistance: Withstands moisture, acids, and chemicals, ideal for food and chemical industries.
- High Tensile Strength: Suitable for piping, boilers, and industrial equipment.
- Weldability: Easily welded and machined for complex designs.
- Temperature Range: Performs well in extreme temperatures, from cryogenic to high-heat applications.
- Sustainability: 100% recyclable with an attractive, glossy finish.
Choosing the Right Stainless Steel
Selecting the appropriate stainless steel grade involves evaluating:
- Environment: Use 316 for high-chloride settings; 304 for general applications.
- Mechanical Requirements: Consider tensile strength and durability needs.
- Aesthetics: Choose glossy or brushed finishes for design purposes.
- Cost and Fabrication: Balance performance with budget and manufacturing needs.
Measuring and Calculating Density
Density is calculated using the formula: Density = Mass / Volume. For 304 stainless steel, with a density of 8.0 g/cm³, weight can be estimated by measuring volume and applying the formula. Digital tools and precise calculators enhance accuracy for engineers and designers.
Tips for Selecting 304 Stainless Steel
- Corrosion Resistance: Ensure it meets environmental conditions, especially in chemical or marine settings.
- Temperature Tolerance: Verify performance up to 870°C (1600°F).
- Weldability: Confirm suitability for welding-heavy projects.
- Strength: Match tensile strength to application demands.
- Standards Compliance: Adhere to standards like ASTM A240 or EN 1.4301 for quality assurance.
Real-World Examples
- Kitchen Equipment: Sinks and bakeware for hygiene and acid resistance.
- Pharmaceutical Tools: Medical trays and surgical instruments for non-reactivity.
- Construction: Cladding and railings for durability and aesthetics.
- Automotive: Trim and exhaust systems for long-lasting performance.
- Chemical Industry: Pipes and tanks for resistance to corrosive substances.
References
-
Material Properties: 304 Stainless (UNS S30400) – NIST – Provides detailed material properties, including density, for 304 stainless steel.
-
Thermophysical Properties of Stainless Steels – OSTI (Office of Scientific and Technical Information) – Includes recommended values for density and other properties of stainless steel types, including 304.
-
Stainless Steel Data Sheet – Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory – Offers comprehensive data on 304 stainless steel, including its density and other specifications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the density of stainless steel 304?
There is no disparate given value for the density of stainless steel 304, but to be of fine usage, the density is expected to be around 8000 kg per cubic meter, or 8.00 grams per cubic centimeter. Having the density allows us to relate weight with volume, a crucial hand in construction and manufacturing of things.
How does the density of stainless steel grade 304 compare to low carbon steel?
It is common knowledge that low carbon steel has a density in the neighbourhood of 7.85 g/cm³. Simply put, the density of low carbon steel is slightly higher than that of 304 stainless steel. The latter is slightly heavier and has a higher density because it includes alloying elements that are not in low carbon steel, such as chromium and nickel, which are when alloyed, in fact enhances mechanical properties and corrosion resistance.
What are the mechanical properties of stainless steel 304?
Stainless steel 304 has fantastic mechanical properties that are characterized by its high tensile strength and ductility. It is part of the austenitic family of stainless steels which make it non-magnetic and have excellent resistance to stress corrosion in its compound. It is also very resistant to heat and oxidants making it an excellent engineering material as it can be used in a wide range of applications.
Is it possible to use the density of 304 grade stainless steel to estimate the weight?
With its density capped at 8.00 g/cm^3, 304 grade stainless steel allows for calculation of its weight in relation to its mass. Hence, it is possible to compute the weight of the material after obtaining the relevant volume. This calculation is particularly relevant in the case of the weight of metal products and the steel plates together with the pipes used in the construction industry.
Could you tell the difference between 304 stainless steel and 304L stainless steel?
About the only real difference in stainless steel is the amount of carbon in it. With 304L, they need it to have less carbide as the weld region is prone to correlating and fighting corrosion. This is especially true of the areas that requires a high amount of carbs to sustain for a long period.
What is 304 stainless steel used for?
Stainless steel 304 is used for a wide array of applications, including household sinks, saucepans, and food processing equipment. It works well in food, kitchen, and chemical industries due to its exceptional corrosion and chemical resistance. It is also used in the construction of buildings because of its excellent strength and useful life.
Why is steel grade 304 so excellent in terms of corrosion resistance?
The steel 304 grade is excellent in terms of corrosion resistance due to its high chromium and nickel content. These materials make the shutdown and corrosion of the metal away due to the formation of a protective layer on the surface, which works in various conditions, such as acidic and basic settings.
What does 304 stainless steel mean when it is identified as UNS S30400?
In reference to 304 stainless steel, the UNS S30400 is the Unified Numbering System designation, which is a very common stainless steel grade. With the designation, the compound’s chemical structure and the mechanical properties are well established, which eases the procurement process in the manufacturing industry.







