When factoring versatility and strength in any material for construction or manufacturing, A36 steel enters the list of popular choices. Considered an economic material due to strength and flexibility, A36 acts as a foundation for the majority of projects stated structural framework up to industrial equipments. Why is it so much used and how do its properties, melting point for instance, affect its functionality in various applications? This guide offers a thorough insight into A36 steel, encompassing areas like chemical composition and mechanical properties, and how this melting point can offset the value of application.
Overview of A36 Steel
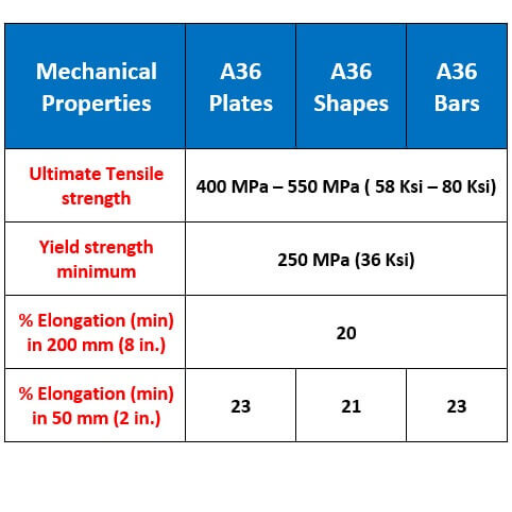
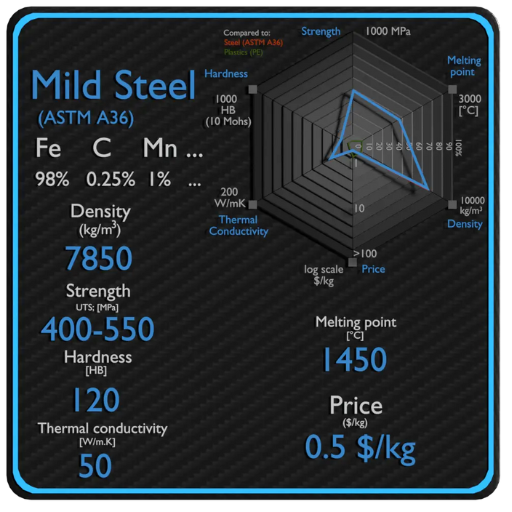
A36 steel is a strong, durable, and cheap carbon steel that finds use in a variety of scenarios. Due to its excellent weldability and formability, it finds use in construction and manufacturing. The steel meets the ASTM standards, thus suitable for structural applications such as bridges, buildings, and load-bearing structures. It has a balanced composition that grants it good mechanical properties, including tensile strength in the range of 58,000 to 80,000 psi, allowing it to accommodate various applications without a hitch to performance.
What is A36 Steel?
The steel A36 is a carbon structural steel that finds extensive use across construction and engineering applications due to its admirable strength-to-weight ratio and being rather cheap. A36 steel has just the right balance of carbon, manganese, phosphorus, sulfur, and silicon, which provides it with favorable mechanical properties such as ductility, weldability, and tensile strength between about 58,000 and 80,000 psi, specified under international ASTM standards.
Key Properties of A36 Steel:
- Tensile Strength: 58,000 – 80,000 psi
- Yield Strength: Minimum 36,000 psi
- Excellent weldability and machinability
- Cost-effective structural material
- ASTM standard compliance
Applications of A36 Steel
A36 steel is used extensively due to high strength, long service life, and maintenance of cost efficiencies. Following are major applications of the steel A36:
Construction of Buildings and Structures
Being able to sustain maximum stress and loads, A36 steel finds an application in the construction of buildings, warehouses, and various structural frameworks. Weldability and machinability permit its use as structural beams, columns, and supports.
Fabrication of Bridges
When it comes to bridge construction, it is chosen for its tensile strength that lies between 58,000 and 80,000 pounds per square inch (psi). Its commendable properties and dimensional adaptability translate into the ability to withstand the weight and environmental stress bridges are subjected to on a daily basis.
Manufacture of Equipment Components
A36 steel is used in the manufacture of plates, bars, and shapes required in machinery and equipment. Its versatility guarantees proper machining and fabrication efficiency to cater to the varied needs of different equipment designs.
Shipbuilding
Shipbuilding utilizes A36 steel for some applications where strength and corrosion resistance, when treated, are of considerable importance. For ships to maintain their structural integrity, they must depend on strong materials under severe marine environments.
Automotive Industry
A36 steel is extensively used for making automotive components, especially frames and other parts that require good strength and durability. In addition, good machinability aids in achieving cost-effective manufacturing processes.
Advantages of A36 Steel
- High Strength and Durability: This steel has excellent tensile and yield strength requirements, thus, it is indeed required in the application of heavy structures and materials subjected to loads and resisting methods. Its yield strength is generally measured at about 36,000 psi (250 MPa).
- Good Machinability: This steel has good machinability allowing it to be cut, drilled, and welded with less effort. This property saves on manufacturing time and cost.
- Cost-Effectiveness: Among selected steel grades that promise high performance, A36 shows more affordably priced yet with good qualities.
- Corrosion Resistance (When Treated): While in raw form A36 steel is prone to rust, its corrosion resistance crosses to higher realms through the application of appropriate treatments such as galvanization or coating.
- Versatility: The versatility of A36 steel has allowed it to gain great popularity in the construction, automotive, and heavy equipment manufacturing industries.
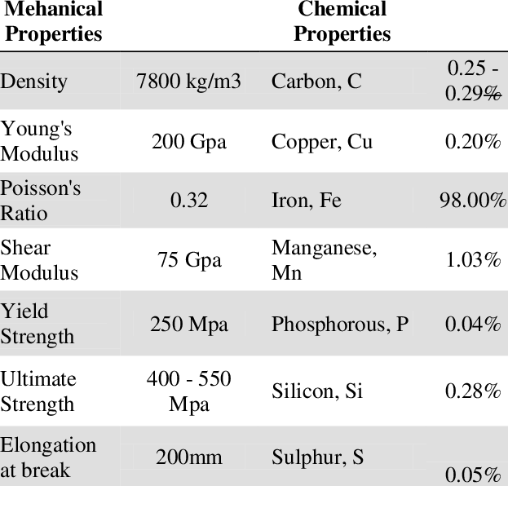
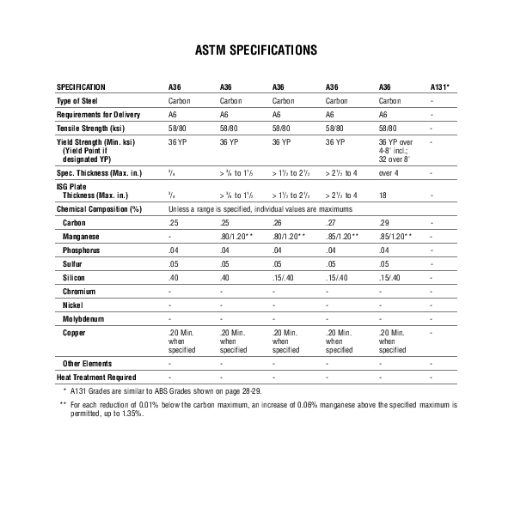
Chemical Composition of A36 Steel
A36 steel is a mixture of elements that are precisely balanced to give the material its notable strength, ductility, and weldability. The approximate chemical constitution by weight is:
| Element | Symbol | Percentage | Purpose |
|---|---|---|---|
| Carbon | C | 0.25% (max) | Given for strength but must be kept low for weldability |
| Manganese | Mn | 0.60-0.90% | Gives hardness and tensile strength |
| Phosphorus | P | 0.04% (max) | Kept low to prevent brittleness |
| Sulfur | S | 0.05% (max) | Limiting it enhances ductility |
| Silicon | Si | 0.40% (max) | Improves strength and toughness |
| Copper | Cu | 0.20% (min, when specified) | Offers corrosion resistance under certain conditions |
Carbon Content and Its Impact
With a critical carbon content in A36 steel affecting its various properties and applications, a carbon content of about 0.26% balances A36 steel’s strength with ductility and weldability. The carbon present in high quantities tends to grant greater hardness and tensile strength to the steel while compromising machining and flexibility. However, the moderate carbon content ensures tensile steel remains sufficiently malleable for further forming and shaping processes.
Melting Point of A36 Steel
The melting point of A36 steel varies usually in the range of 2,500-2,800°F (1,370 to 1,540°C). Due to the variation in steel composition, mainly iron in large quantities, with some carbon, manganese, and other elements in minor quantities, the exact melting point varies slightly.
Factors Affecting the Melting Point
The melting point of an A36 steel is influenced by innumerable factors, most of them related to composition or environment:
- The presence of alloying elements such as carbon or manganese tends to alter slightly the melting range
- A higher carbon content will tend to lower the melting temperature slightly
- Impurities or inclusions within the material can also interfere with its thermal properties
- External influences, like the rapid rate of heat application or exposure to certain chemicals
Comparison of Melting Points with Other Carbon Steels
| Steel Grade | Carbon Content | Melting Point (°F) | Melting Point (°C) |
|---|---|---|---|
| A36 Steel | 0.25% max | 2,500-2,800 | 1,370-1,540 |
| 1018 (Low Carbon) | 0.18% max | 2,570 | 1,410 |
| 1045 (Medium Carbon) | 0.45% | 2,600 | 1,426 |
| 1095 (High Carbon) | 0.95% | 2,500 | 1,370 |
Performance at High Temperatures
As a mild carbon steel, A36 steel possesses sufficient qualities for a broad variety of industrial applications. Generally, A36 steel retains its structural integrity up to an upper temperature limit:
- Up to 650°F (343°C): Retains acceptable performance
- Around 1000°F (538°C): Yield strength reduction begins
- Beyond 650°F: Oxidation sets in, lowering tensile strength and causing warping
Applications in High-Temperature Environments
Boiler Components
Boiler components made from A36 steel withstand great temperatures and pressures for functioning reliably in power generation and industrial heating systems.
Furnace Structures
The material finds use in furnace constructions because it does not deform or fail even after being subject to prolonged periods of elevated heat.
Heat Exchangers
A36 steel finds its place in some heat exchanger components, and its thermal properties help maintain the thermal transfer in an uninterrupted manner.
Industrial Kilns
Since A36 steel is resilient to high temperature, the material finds use in numerous industrial kilns for ceramics, metallurgy, and chemical manufacturing.
Steam Piping Systems
It is used in the steam pipeline to carry high-temperature steam, ensuring durability and safety even under incipient stresses.
Heat Treatment Processes for A36 Steel
The heat treatment of A36 steel involves various methods to give it a special property for a particular use:
| Process | Temperature Range | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Annealing | 1,500°F – 1,700°F | Make the material soft and easy in machining |
| Normalizing | 1,650°F – 1,900°F | Increase strength while refining grain size |
| Stress-Relief | 1,100°F – 1,300°F | Minimize internal stresses from welding or machining |
Fabrication and Use of A36 Steel Plate
A36 steel plate is selected for general purpose applications due to the balanced mechanical property and easy fabrication of the material. Fabrication involves such processes as:
Fabrication Techniques for A36 Steel
- Welding: A36 can be welded with all conventional welding techniques like MIG, TIG, and stick welding. Usually, it does not require pre-heating.
- Cutting: The cutting methods used often include plasma cutting, laser cutting, and oxy-fuel cutting.
- Machining: A36 steel machines easily using conventional machining tools. It undergoes drilling, milling, and tapping easily.
- Forming: Due to the excellent ductility of this steel, it can be bent, rolled, or pressed into a variety of shapes without fear of cracking or fractures.
Industry Applications of A36 Steel Plates
- Construction and Infrastructure: For bridges, buildings, and infrastructural undertakings
- Shipbuilding Industry: For making hulls and other ship parts
- Automobile Manufacturing: For automotive parts like chassis, brackets, and frames
- Machinery and Equipment: For heavy machinery and industrial equipment construction
- Oil and Gas Industry: For storage tanks, drilling platforms, and pipelines
References
-
Fracture Toughness and Charpy CVN Data for A36 Steel with Wet Welding – Academia.edu – Discusses the melting point of A36 steel and its behavior under welding conditions.
-
Structural Properties of Steels Subjected to Multiple Cycles – Purdue University – Examines the thermal limits and structural properties of A36 steel under high temperatures.
-
Study of Cold-Formed Steel Structural Members Made of A36 Steel – Missouri S&T Scholars’ Mine – Provides detailed data on the structural properties of A36 steel.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the melting point of A36 steel?
The melting point of A36 steel ranges between 2600°F and 2700°F (1425°C and 1482°C). The very high melting point offers strength and durability for all structural applications.
What are the mechanical properties of A36 steel?
It has excellence in mechanical properties, with a yield strength minimum value of 36 ksi and an ultimate tensile strength varying between 58-80 ksi. This set of properties makes A36 widely used in construction and manufacturing.
What is the chemical composition of A36 steel?
It is composed of the lowest carbon content, usually about 0.26% maximum, manganese from 0.60-0.90%, along with traces of phosphorus and sulfur. This composition assures good weldability and machinability.
How is A36 steel fabricated?
A36 steel can be fabricated through a variety of methods depending on the nature of the intended application including welding, cutting and machining. The very good weldability of A36 steel allows it to be joined quite easily and fabricated into structural components.
What are the advantages of using A36 steel?
Its advantages include being economically priced, possessing high strength, and being suitable for numerous structural applications. Furthermore, due to its low carbon content, it also has good ductility and toughness.
What are the physical properties of A36 steel?
The physical properties of A36 steel include a density of approximately 490lb/ft^3 and good corrosion resistance when treated properly. These are the properties that enhance its suitability across different environments.
How does the ASTM specification relate to A36 steel?
The ASTM specification for A36 steel known as ASTM A36 laid down the standard specifications for carbon structural steel. It is this specification that ensures the steel A36 shall meet certain mechanical and chemical property standards.
What is the relation of A36 steel with low carbon steel?
A36 is classified as a low carbon steel, which means that it has a carbon content of less than 0.3%. Hence, it is these properties that allow it enhanced weldability and more ductility.
What is the yield strength of A36 Steel?
The A36 steel yield strength minimum value is 36 ksi, which gauges how much stress A36 steel can take without deforming permanently. This evidence ensures the structural integrity of its use in construction applications.