When it comes to industrial applications, the selection of the right materials can significantly impact both performance and reliability. Among the most commonly used options, the DIN 11850 stainless steel pipe and the bright tube stand out as highly specialized components, each catering to specific operational requirements. This article dives into the critical differences between these two types of tubing, offering a detailed comparison of their material composition, manufacturing standards, and functional uses. By understanding these distinctions, engineers, manufacturers, and procurement specialists can make more informed decisions, ensuring the best fit for their specific applications. Whether you are focused on durability, hygiene, or precision, this guide will provide the essential insights you need to optimize your material choices.
What Is the Din 11850 Product Standard?

The DIN 11850 product standard specifies the dimensions, tolerances, and technical delivery conditions for stainless steel tubes used in the food, chemical, and pharmaceutical industries. It is designed to ensure compatibility, reliability, and hygiene in piping systems. This standard primarily addresses the uniformity of tube diameters, wall thicknesses, and surface finishes, facilitating easier integration and maintenance of piping components across various applications.
Understanding DIN 11850 Tube Specifications
Key Features of DIN 11850 Tubes
DIN 11850 tubes are characterized by precise dimensional standards that ensure consistency across diverse applications. The outer diameters range from 10 mm to 305 mm, with standardized wall thicknesses designed to balance strength and flow capacity. Surface finishes typically adhere to strict roughness specifications, often ≤ 0.8 µm for enhanced hygiene and corrosion resistance. These tubes are commonly fabricated from stainless steel grades such as 1.4301 (AISI 304) or 1.4404 (AISI 316L), offering durability, chemical resistance, and suitability for sanitary environments. This standard simplifies system integration and maintenance, meeting the rigorous demands of food, chemical, and pharmaceutical industries.
Key Features of DIN 11850 Stainless Steel Pipe
- High-Quality Surface Finish
DIN 11850 pipes feature a polished surface finish, typically with a roughness (Ra) of ≤ 0.8 µm, ensuring compliance with stringent hygiene and cleaning requirements. This makes them ideal for use in industries where sanitary conditions are critical.
- Material Composition
Constructed from premium stainless steel grades such as 1.4301 (AISI 304) and 1.4404 (AISI 316L), these pipes offer excellent resistance to corrosion, chemical exposure, and high-pressure environments. Grade 1.4404 (AISI 316L) is specifically designed for enhanced resistance to chlorides and corrosive media.
- Dimensional Standards
The dimensions of DIN 11850 pipes, including internal diameter (ID) and external diameter (OD), are standardized for seamless integration into piping systems. Common diameter ranges (outer diameter) include 10 mm to 305 mm, with corresponding wall thicknesses tailored for pressure ratings and system requirements.
- Compatibility and System Integration
These pipes are compatible with standardized fittings and connections, simplifying installation and reducing assembly time. They are particularly suited for CIP (Clean-in-Place) and SIP (Sterilization-in-Place) systems in critical processes.
- Mechanical Strength
DIN 11850 pipes have excellent mechanical properties, such as tensile strength typically in the range of 500–700 MPa and yield strength above 200 MPa, depending on the specific stainless steel grade used. This ensures structural reliability under operational pressures.
- Versatility and Applications
These pipes are versatile and widely used in food and beverage processing, pharmaceutical manufacturing, biotechnology, and chemical industries due to their ability to maintain product integrity and meet safety standards.
By integrating these technical parameters, DIN 11850 stainless steel pipes guarantee performance, reliability, and compliance with industry-specific requirements.
Applications in the Sanitary Industry
- Food and Beverage Processing Lines – Ensures the hygienic transportation of liquids such as milk, juices, and processed foods, maintaining purity and preventing contamination.
- Pharmaceutical Production Systems – Facilitates the transfer of pharmaceutical-grade fluids while adhering to exacting cleanliness standards critical for drug manufacturing.
- Biotechnology Equipment – Supports sterile environments required for processes like fermentation or cell culture by providing corrosion-resistant and easy-to-clean piping systems.
- Brewing and Distillation Systems – Used in breweries and distilleries for transferring ingredients and products, ensuring taste integrity and compliance with health regulations.
- Chemical Processing Plants – Suitable for carrying sensitive or reactive chemicals safely, owing to their durability and resistance to chemical erosion.
How Does a Bright Tube Differ from a DIN 11850 Tube?

A Bright Tube differs from a DIN 11850 Tube primarily in terms of manufacturing process, surface finish, dimensional tolerances, and application suitability.
|
Parameter |
Bright Tube |
DIN 11850 Tube |
|---|---|---|
|
Manufacturing |
Cold-drawn |
Welded |
|
Surface Finish |
High polish |
Standard |
|
Tolerances |
Tight |
Flexible |
|
Corrosion |
High resistance |
Moderate |
|
Standards |
Customizable |
DIN compliant |
|
Application |
Specialized |
General-purpose |
Characteristics of a Bright Annealed Tube
A bright annealed tube is manufactured using a high-precision cold-drawing process, followed by heat treatment in a controlled atmosphere to achieve the desired mechanical and surface properties. This process results in a smooth, highly reflective surface finish that minimizes surface contamination and prevents particle entrapment, making it ideal for critical applications.
Key Technical Characteristics:
1. Manufacturing Process:
-
- Cold-drawn followed by annealing under a vacuum or inert gas, ensuring a bright surface without oxidation.
- Surface Finish:
- Ra ≤ 0.4 μm (or higher as required).
- Superior polishing enhances cleanliness and reduces the risk of contamination.
- Dimensional Tolerances:
- Tight tolerances, often up to ±0.02 mm, ensuring precision for applications requiring high accuracy.
- Corrosion Resistance:
- High corrosion resistance due to the preservation of the passive layer during the bright annealing process. Typically made from high-grade stainless steels such as 316L or 304.
- Mechanical Properties:
- Yield Strength (depending on grade): Approximately 205-515 MPa.
- Tensile Strength (depending on grade): Approximately 485-600 MPa.
- Standards Compliance:
- Can be customized to meet standards such as ASTM A269, ASTM A213, or EN 10216-5 as per application needs.
- Applications:
- Commonly used in industries such as pharmaceuticals, semiconductors, food and beverage, and chemical processing due to its excellent surface finish, corrosion resistance, and purity.
These characteristics make bright annealed tubes suitable for environments where hygiene, precision, and resistance to aggressive media are critical.
Comparing Polish and Finish
Polish and finish, though often used interchangeably, serve distinct roles in determining the surface quality and performance of materials such as stainless steel. Polish refers specifically to the mechanical process of smoothing and refining the surface using abrasives or polishing compounds. The goal is to reduce surface roughness and achieve a desired level of smoothness, typically measured in terms of Ra (Roughness Average). Polished surfaces are classified based on the grit level used, with finer grits producing smoother finishes.
On the other hand, Finish encompasses the overall surface treatment, including polish, texture, and any post-treatment processes (such as chemical passivation or electropolishing) that improve corrosion resistance and aesthetic appearance. Finishes are standardized and categorized, such as 2B, No. 4 (brushed), and BA (bright annealed), to indicate varying textures and reflectivity levels. The selection of a specific finish depends on the intended application, balancing factors like hygiene, durability, and visual appeal.
Understanding the differences between polish and finish is critical, as they directly impact performance in demanding industries. For instance, a polished surface is essential for minimizing particulate contamination in semiconductor manufacturing, while a specific finish like No. 4 is optimal for food-grade environments requiring easy cleaning and a non-reflective surface.
Usage in Food Industry Stainless Steel Applications
- Storage Tanks and Vessels: Stainless steel is widely used for constructing storage tanks due to its corrosion resistance, ensuring the safe containment of liquids and ingredients without contamination.
- Food Processing Equipment: Equipment such as mixers, grinders, and conveyor systems rely on stainless steel for its durability and ability to meet stringent sanitary standards.
- Work Surfaces and Preparation Tables: Stainless steel surfaces are essential in food preparation areas as they are non-porous, resist bacterial growth, and are easy to clean and maintain.
- Piping Systems: Stainless steel piping is commonly used for the transport of liquids, such as milk or juices, as it resists corrosion and prevents leaching of contaminants into the products.
- Cooking and Baking Utensils: High-grade stainless steel is used in cookware, baking trays, and utensils due to its heat resistance, non-reactive properties, and longevity under rigorous use.
What are the Benefits of Stainless Steel Tubes?

Stainless steel tubes offer a range of benefits due to their unique properties. They are highly resistant to corrosion, making them ideal for use in environments exposed to moisture, chemicals, or extreme temperatures. Their durability ensures long service life with minimal maintenance, reducing replacement and repair costs. Stainless steel tubes also maintain structural integrity under high pressure and exhibit excellent mechanical strength, allowing for versatile applications in industries like construction, transportation, and food processing. Additionally, they are non-reactive with many substances, ensuring safety and cleanliness in applications involving food, beverages, or pharmaceuticals.
Advantages of Using 304 and 316L Stainless Steel
- Corrosion Resistance – Both 304 and 316L stainless steel exhibit excellent resistance to corrosion, with 316L offering superior protection against pitting and crevice corrosion due to its higher molybdenum content, making it ideal for marine and chemical environments.
- Durability and Strength – These grades are highly durable and maintain structural integrity under extreme conditions, including high pressure and temperature, ensuring reliability in demanding industrial applications.
- Hygienic Properties – The smooth surface finish of 304 and 316L stainless steel prevents bacterial growth, making them ideal for use in food processing, pharmaceutical, and medical equipment where hygiene is critical.
- Weldability and Versatility – Both grades are highly weldable and can be easily fabricated into a variety of shapes and forms, allowing for versatile applications across industries like construction, automotive, and aerospace.
- Low Maintenance and Longevity – These stainless steels resist tarnishing and wear over time, minimizing maintenance requirements and significantly extending the lifespan of components, reducing overall operational costs.
Importance of Hygienic Design
Hygienic design plays a critical role in ensuring safety, efficiency, and regulatory compliance across various industries, particularly in food processing, pharmaceuticals, and healthcare. Effective hygienic design minimizes the risk of contamination by eliminating crevices, sharp angles, or other areas where bacteria and debris could accumulate. Materials such as stainless steel are commonly used due to their non-porous surfaces, corrosion resistance, and ease of cleaning, ensuring long-term durability in demanding environments.
Properly designed equipment and facilities simplify cleaning processes, reducing downtime, promoting operational efficiency, and ensuring adherence to stringent sanitation standards like those outlined by the FDA or EHEDG. Furthermore, hygienic design is indispensable for achieving high product quality and maintaining consumer trust, as it directly impacts the integrity of products and the prevention of cross-contamination or allergen exposure. Employing these principles helps safeguard public health while enhancing overall production performance.
How Does Weld Quality Impact Tube Performance?
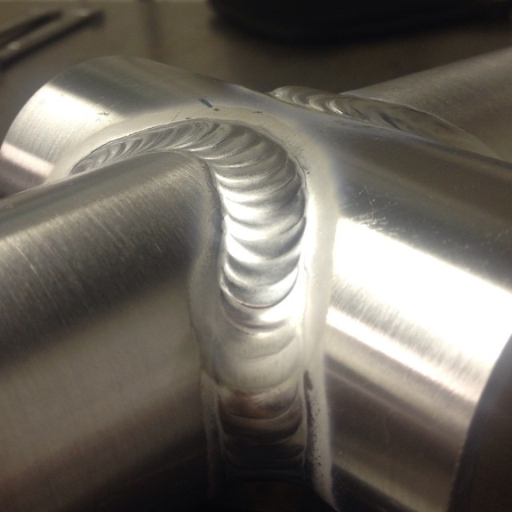

Weld quality is a critical determinant of tube performance across various industrial applications. High-quality welds ensure structural integrity, preventing weaknesses that could lead to failures under pressure, thermal stress, or mechanical strain. Properly executed welds enhance durability by eliminating potential defects such as porosity, inclusions, or incomplete fusion, which can compromise the tube’s strength and reliability. Additionally, superior weld quality minimizes turbulence and flow restrictions in fluid transport applications, maintaining operational efficiency and reducing wear over time. Consistent weld quality also ensures compliance with industry standards, supporting safety and performance in demanding environments.
Differences Between Welded and Seamless Tubes
Welded tubes are manufactured by rolling and welding flat strips of metal, resulting in a visible seam, while seamless tubes are created through extrusion processes without any seams, which often makes them stronger and better suited for high-pressure applications.
|
Parameter |
Welded |
Seamless |
|---|---|---|
|
Manufacturing |
Rolled/Welded |
Extruded |
|
Seam Presence |
Visible |
None |
|
Strength |
Moderate |
High |
|
Cost |
Lower |
Higher |
|
Pressure Handling |
Moderate |
Excellent |
|
Size Range |
Limited |
Wide |
|
Surface Finish |
Consistent |
Less Uniform |
|
Production Speed |
Faster |
Slower |
|
Applications |
General |
Critical |
This table concisely highlights the key differences between welded and seamless tubes across various critical parameters.
Ensuring Strong Weld Integrity
Ensuring strong weld integrity demands a comprehensive understanding of material characteristics, welding techniques, and quality control measures. First, I always ensure the proper selection of compatible base metals and filler materials to avoid issues like cracking or weak joints. Rigorous preparation of the surfaces, including cleaning and beveling, is crucial to achieving optimal fusion and penetration. During welding, I consistently monitor parameters like heat input, travel speed, and shielding gas control, as these directly affect the strength and uniformity of the weld. Post-welding inspections, such as non-destructive testing (NDT), allow me to identify and address any potential flaws. By adhering to industry standards and employing advanced techniques, I maximize weld quality and reliability for both general and critical applications.
Why is Polished Sanitary Finish Crucial?

A polished sanitary finish is crucial in environments where cleanliness and hygiene are paramount, such as food processing, pharmaceutical, and healthcare industries. This finish minimizes surface roughness, reducing the risk of contamination by eliminating crevices where bacteria or other microorganisms could thrive. Additionally, it enhances durability and makes cleaning and maintenance more efficient, ensuring compliance with stringent industry standards and regulations. Achieving a polished sanitary finish ensures both operational safety and product integrity.
Meeting Sanitary Requirements
Meeting sanitary requirements in the food processing, pharmaceutical, and healthcare industries involves adhering to strict standards designed to maintain hygiene and prevent contamination. Surfaces and equipment must be constructed using materials that are corrosion-resistant, non-toxic, and capable of withstanding rigorous cleaning procedures. Stainless steel is a preferred material, particularly with a polished sanitary finish that ensures surfaces are smooth and free from microscopic crevices.
Standards like those set by the FDA, USDA, and ISO require that all equipment complies with cleanability and durability regulations. Proper cleaning protocols, such as CIP (Clean-In-Place) systems, are often implemented to maintain consistent hygiene without disassembly of equipment. Additionally, regular inspections, documentation of cleaning processes, and adherence to materials compatibility guidelines are critical components of meeting these stringent sanitary requirements. These measures not only safeguard operational safety but also ensure compliance and product quality.
Achieving the Desired Roughness Average
Achieving the desired Roughness Average (Ra) requires a combination of precise material selection, meticulous surface finishing techniques, and ongoing quality assurance processes. We prioritize the use of advanced polishing methods, including mechanical and electropolishing, to achieve the required surface smoothness while minimizing imperfections. By leveraging cutting-edge metrology tools for Ra measurement and adhering to industry standards, we ensure surfaces meet the necessary specifications for hygiene, durability, and performance. Continuous monitoring and refinement of our processes are vital to maintaining consistent results and exceeding industry expectations.
Reference Sources
- Alfa Laval – Hygienic DIN 11850 Tubes
- Aalco – General Information on Stainless Steel Hygienic Tubes and Fittings
- Made-in-China – DIN 11850 Standard Stainless Steel Food Grade Pipe and Tube
- SKS – Hygienic Tube & Process Components
- UKIRS – EN 10357 Standard Replacing DIN 11850
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: What is the main difference between a DIN 11850 stainless steel pipe and a bright tube?
A: The main difference lies in their applications and finishes. DIN 11850 stainless steel pipes are typically used in sanitary applications due to their high-quality and strict quality control, whereas bright tubes are often used in decorative applications due to their polished surface.
Q: How does a seamless steel pipe differ from a stainless steel welded pipe?
A: Seamless steel pipes are made without any welding seams, offering better pressure resistance and strength, whereas stainless steel welded pipes are made by welding a seam along the length, which can be more cost-effective and suitable for larger diameters.
Q: What are the advantages of using seamless pipe tube in heat exchangers?
A: Seamless pipe tubes are preferred in heat exchangers due to their higher pressure resistance and ability to withstand high temperatures, ensuring efficient heat transfer and longer life span of the heat exchanger.
Q: Why is precision important in the manufacturing of tube stainless steel?
A: Precision is crucial in tube stainless steel manufacturing to ensure that the tubes match tolerances and fit perfectly in their applications, such as in fittings and reducers, which enhances the system’s integrity and performance.
Q: What role does the outer diameter (OD) play in choosing a pipe seamless?
A: The outer diameter (OD) is essential in selecting a pipe seamless as it determines the pipe’s compatibility with existing systems and fittings, ensuring proper flow and system efficiency.
Q: What is the significance of a crevice-free design in stainless steel welded pipes?
A: A crevice-free design in stainless steel welded pipes helps prevent the accumulation of bacteria and debris, making them ideal for sanitary applications where hygiene is a priority.
Q: How does the bend radius affect the performance of reducers and tubes?
A: The bend radius is critical in determining the flow rate and pressure drop within reducers and tubes. A suitable bend radius ensures smooth flow and minimizes turbulence, which is essential for maintaining system efficiency.
Q: What are the common finishes available for tube stainless steel?
A: Tube stainless steel is available in different finishes, including matte, polished, and satin, each offering varying levels of reflectivity and surface texture to suit specific aesthetic and functional requirements.
Q: What are the benefits of using high-quality tube stainless steel in manufacturing and distribution systems?
A: High-quality tube stainless steel provides durability, resistance to corrosion, and a seal of quality that ensures long-term performance and reliability in manufacturing and distribution systems.
Q: How does strict quality control impact the supply of stainless steel welded pipes and seamless pipe tubes?
A: Strict quality control ensures that both stainless steel welded pipes and seamless pipe tubes meet industry standards, reducing the risk of defects and failures, and ensuring a consistent supply of high-quality products for various applications.