HY-80 steel plate has acquired the status of a legend in the engineering world for its strength and versatility, which are the most sophisticated environments. Submarine building, offshore platform construction, and the development of high-performance machinery are some of the applications where HY-80 is recognized as the key material due to its particular features, thus being a frontrunner in critical uses. Made to withstand immense pressure and abrasion, this extraordinary metal not only has a long life but also can be tough, hence, making it very reliable in the toughest situations. All you need to know about HY-80 steel plate will be discussed in the following guide, including its main features, impressive advantages and the vast array of industries that rely on it.
Introduction to HY-80 Steel

What is HY-80 Steel?
HY-80 steel is a low-alloy, high-strength steel developed with extraordinary properties of toughness, durability, and resistance to very high stress. Originally developed for military and naval purposes, it has become known for its use in extreme conditions like underwater environments and high pressure situations.
🔍 Understanding the “HY-80” Designation
HY = “High Yield” – referring to the steel’s exceptional yield strength
80 = Yield strength of approximately 80,000 psi (80 ksi)
This high yield strength guarantees that the metal will not lose shape even when subjected to substantial loads, ensuring structural integrity under extreme conditions.
In addition, the HY-80 steel has great welding and cracking resistance qualities, which makes it very suitable for shipbuilding, submarines, and other heavy-duty engineering projects where safety and reliability are first and foremost.
HY-80 Steel Material Properties
The HY-80 steel allures with its remarkable strength, long life, and flexibility, and hence, it is a popular choice for challenging applications. Its mechanical properties reveal performance characteristics so exceptional that they actually make the steel differ from the regular structural steels.
⚗️ Chemical Composition
The chemical composition of HY-80 steel commonly comprises carbon, manganese, nickel, chromium, molybdenum, and impurities—each one specifically added in small amounts in order to give the steel hardness, corrosion resistance and strength at the same time. This exact mixture is vital for the steel to be able to perform at the highest possible levels in the most demanding conditions which are in deep-sea applications and high-pressure environments.
The Significance of Strength and Toughness in Naval Applications
Ships working in difficult sea surroundings would have to depend only on the qualities of the steel used in their making to ensure security and endurance. During the entire lifetime of such steel, its mechanical properties, impact, pressure, and vibration are met, and it has to perform without breaking down.
💪 Strength Benefits
- Withstands enormous mechanical stress
- Maintains structural integrity under load
- Optimal strength-to-weight ratio
- Prevents deformation in service
🛡️ Toughness Benefits
- Absorbs impact energy effectively
- Reduces risk of catastrophic failures
- Prevents fracture propagation
- Superior ductility characteristics
Control over microstructure during steel production has been recognized in the latest studies as a significant contributor to the improvement of the strength-to-ductility ratio. Ship designers and builders rely on these characteristics to enable ships to withstand the most demanding conditions, from high-pressure depths for submarines to extreme weather for surface ships, while maintaining the highest reliability and safety.
Strength and Toughness of HY-80 Steel

Yield Strength Overview
The yield strength of a material is the stress point at which it begins to deform permanently or plastically. For example, in the case of HY-80 steel, this property is the main reason for its use in naval industry and also sets the maximum stress level for the steel to undergo permanent deformation without cracking.
HY-80 Yield Strength
80,000 PSI
(80 ksi)
This high-performance characteristic is essential for construction of military submarines and surface ships where exceptional durability is required. The structural integrity secured under huge stress leads to safety and reliability in harsh marine environments.
Impact Toughness Properties
The outstanding impact toughness of HY-80 steel is one of the main characteristics of this steel grade, which means that the material can take up and release the energy even in harsh and extreme conditions without the formation of cracks. According to recent studies and published data, the toughness of HY-80 steel is so high that it can not only withstand dynamic loads but also retain its strength at very low and high temperatures.
🔬 What Enables Superior Toughness?
- Strict control of alloy composition: Precise balance of nickel, chromium, and molybdenum
- Specialized heat treatment processes: Optimizes microstructure for impact resistance
- Tempered martensite structure: Provides combination of strength and toughness
- Low-temperature performance: Maintains properties in cold marine environments
These features highlight HY-80 steel’s importance in critical applications where rapid mechanical shocks and impacts are frequent, assuring operational reliability and safety.
Comparison with Standard Steel Plates
When compared to standard structural steel plates such as A36 or ASTM A516, HY-80 offers superior tensile strength and fracture toughness, making it the preferred choice for demanding applications.
⚡ Why HY-80 Outperforms Standard Steels
HY-80 stee l is specifically made for top-stress applications like submarines and battleships. It can go through severe pressures and quench and temper very fast. Compared to conventional steels, HY-80 is subjected to severe heat treatment and nickel plus molybdenum addition improves the strength of the steel dramatically. Therefore, HY-80 is the most preferred material in crucial activities where safety and reliability are the main issues.
Weldability of HY-80 Steel

Welding Techniques for HY-80
There is a high requirement for accuracy and strict compliance to certain techniques in the process of welding HY-80 steel in order to avoid degrading the material’s mechanical properties and compromising its structure. The most important factors in dealing with the strongest and most ductile material are preheating, controlling the temperature between passes, and performing post-weld heat treatment (PWHT).
Preheat and Interpass Temperatures
The risk of hydrogen cracking is minimized by preheating HY-80 steel to a temperature of about 100°F to 250°F, the exact temperature depending on the thickness of the metal piece. Controlling interpass temperatures in this way not only guarantees the quality of the weld but also reduces stress during the process.
Suitable Welding Processes
Welding techniques that are predominantly applied to HY-80 are Shielded Metal Arc Welding (SMAW) and Gas Tungsten Arc Welding (GTAW). The aforementioned techniques enable accurate control of heat input, hence the effects of distortion are minimized and metallurgical stability is guaranteed.
Filler Material Selection
Choosing the appropriate filler material is essential. The strength and toughness of filler metals should be the same as that of the base metal. HY-80 filler materials contain AWS A5.5 E10018 and E11018 electrodes which are recognized for their high strength and low hydrogen traits.
Post-Weld Heat Treatment (PWHT)
Heat treatment to relieve residual stresses and improve toughness of the steel is usually performed on the weld area. The welded structure is heated to a predetermined temperature and subsequently cooled at a controlled rate.
✅ Critical Success Factor: These techniques implemented with care ensure successful welding of HY-80 steel while maintaining the critical properties that guarantee performance in tough environments.
Challenges in Welding HY-80 Steel
Welding HY-80 steel presents significant challenges due to its unique chemical composition and mechanical properties. Understanding these challenges is essential for achieving high-quality welds.
🚀 Technological Advances in HY-80 Welding
Innovative technologies from recent times show that state-of-the-art welding techniques, for instance, automated submerged-arc and laser welding, can make the process less complicated by granting more control over the heat applied and the quality of the weld. Technologies that allow real-time monitoring assist in spotting welding defects earlier on, hence, reducing reworking and ensuring uniformity.
Notwithstanding these developments, the welding of HY-80 steel still relies on the presence of expert welders, adherence to welding processes, and implementation of strong quality control measures.
Best Practices for Successful Welding
Following best practices while welding HY-80 steel or other challenging alloys is crucial if high-quality welds meeting safety and performance standards are to be achieved.
✓ Pre-Welding Practices
- Preheat material appropriately (100-250°F)
- Ensure proper joint preparation
- Verify filler material compatibility
- Control environmental conditions
✓ During Welding
- Employ multi-pass welding techniques
- Regulate interpass temperatures
- Control heat input precisely
- Use real-time monitoring technology
✓ Post-Welding Practices
- Perform PWHT when necessary
- Conduct non-destructive testing
- Comply with AWS/ASME standards
- Document all procedures thoroughly
📚 Industry Insights
Search trends show that there is more focus on sophisticated training programs for welders which means that skill operators are very important when working with difficult materials like HY-80 steel. The people who keep abreast of the changes in the industry and go for the new welding techs in their processes are the ones who enjoy the highest success rates and even get the welds that are most reliable and performing well to be done.
Applications of HY-80 Steel
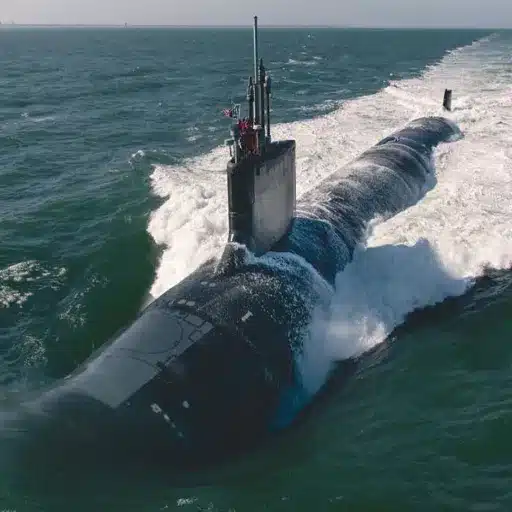

Naval Applications and Submarine Construction
Using HY-80 steel in navy operations is really crucial. This is mainly due to the fact that it is used to manufacture submarines and other warships. The material’s excellent strength and very good durability qualities make it ideal for enduring the heavy pressure and the bad conditions existing under the water.
🚢 Why HY-80 is Essential for Naval Construction
⚓ Pressure Resistance
It can withstand high pressures at various depths without compromising its structure.
🔧 Weldability
Enables complex and robust designs without risking overall structural strength
🛡️ Durability
Maintains integrity throughout service life in harsh marine environments
💪 Toughness
Absorbs impact energy and resists crack propagation under dynamic loading
The public is getting more and more curious about the modern submarine building materials and techniques, though the increase is gradual and slow. On a global scale, the increase of naval power is being recognized as a factor that will determine the countries’ ability to keep their superiority and thus, it is considered a strategic factor. Professional welders who are thoroughly trained in HY-80 steel and modern welding technology are applying skilled welding that results in tougher and more reliable submarines. This cooperation highlights the necessity of continuous education and innovation in naval construction to match the changing demands and the security challenges of the industry.
Other Industrial Applications
HY-80 steel is generally recognized for its use in naval construction, but it has considerable applications in other sectors as well. Due to its extraordinary strength and high-stress tolerant nature, it is the material selected for various hard applications.
🌱 Emerging Trends in Industrial Applications
The modern engineering and material science breakthroughs have played a crucial role in the progressive adoption of the HY-80 steel in the oil and gas sector, where materials are subjected to extreme conditions and must perform flawlessly. Recent statistics point at an increasing interest in the application of HY-80 steel in the renewable energy industry, primarily for the production of strong wind turbine components. This development is in line with the industry’s shift towards the use of durable materials in their quest for sustainable and highly-efficient technologies.
Case Studies in the Defense Sector
There is a large number of case studies in the defense sector, but one important case study is looking at the application of advanced composite materials and high-strength alloys to develop ultra-light, high-strength armoring for military vehicles. It appears that the public is getting more and more interested in materials that are designed for better ballistic protection but at the same time, the weight of the vehicle is reduced.
🎯 Defense Sector Innovations
- Military Vehicles: Advanced composite materials combined with HY-80 for ultra-light, high-strength armoring
- Personal Body Armor: Cutting-edge alloys and ceramics for lightweight, strong, and protective equipment
- Strategic Focus: Global defense initiatives aimed at increasing mobility and energy efficiency without compromising safety
- Performance Standards: New benchmarks for resilience and adaptability in the harshest operational conditions
Through the use of these advanced materials, defense agencies are not merely establishing new standards for performance but also setting unprecedented levels of operational effectiveness.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the submarine and navy applications of HY-80 steel?
The main application of HY-80 steel in submarines is for the building of skeletal and pressure hulls since it has very high yield strength (up to 80 ksi) and toughness at the same time. This guarantees that submarines are able to endure extremely high water pressure as well as heavy loads without getting damaged. The steel’s low-carbon and low-alloy content give it a good mix of hardness and ductility which help in the preservation of high fracture toughness thus no brittle fracture will occur. The steel used for the marine application is required to have at least the minimum yield strength—80 ksi in the case of HY-80—and the notch toughness necessary for marine service. HY-80 steel has found wide applications in the construction of ships and submarines since it has the necessary mechanical properties for underwater use and resistance to fatigue. The alloying and welding are done under stringent conditions to ensure the desired microstructure is achieved and to avoid the formation of unstable martensite that can cause reduction in impact strength.
What are the tensile properties and minimum yield strength for HY-80 steel plates?
The minimum yield strength of HY-80 alloy is around 80 ksi, which is one of the main mechanical properties for this steel. This ultra-low alloy steel can tolerate and deform to the level of 80 ksi without taking permanent damage, thus it is suitable for hurricane-proof constructions and pressure vessels. The steel performance is evaluated through testing to ascertain yield, ultimate tensile strength and elongation for the requirement of ductility. ASTM and industry sources like ASM International provide standards for acceptable ranges of physical properties and strain rates in testing. Knowing these parameters helps engineers to ensure mechanical integrity in the construction of ship and submarine, and in other naval applications as well.
How does the microstructure influence the fracture toughness of HY-80 and HY-100?
The microstructure of HY-80 and HY-100 steels basically determines their fracture characteristics, toughness, and ductility. Typically, the martensite phase is tempered for the sake of the desired combination of strength and high fracture toughness. HY-80’s toughness can be significantly reduced if the presence of untempered martensite occurs during improper welding or heat treatment, as this may lead the material to be softer and hence more susceptible to impact failure rather than ductile fracture. The thermal cycles on HY-100 and HY-130 can be a source of discrepancies in hardness and notch toughness which underlines the importance of controlling the welding parameters and post-weld heat treatment. Notch toughness testing and fracture mechanics are among the methods performed during the investigation of the HY-80 fracture characteristics to guarantee that the material behaves as expected under different strains and high loads. Selecting the right low-alloy combinations along with heat treatments is the way to go in the optimization of microstructure in naval applications such as pressure hulls and submerged-arc welding processes.
What welding considerations affect the weldability of HY-80 steel plates?
Weldability of HY-80 steel thermally treated involves the strict control of preheated, interpass and post-weld heat treatment temperatures, which to avoid the hard, untempered martensite formation, as well as to keep the notch toughness in the heat-affected zone. Different ships and submarines’ manufacturing including submerged arc welding and other common processes necessitate specific welding parameters settings for guaranteeing mechanical integrity and eliminating cracking risk. Additionally, HY steel including HY-80 can be prone to hydrogen-induced cracking, thus low-hydrogen electrodes, and consumables proper baking are needed to maintain impact strength not compromised. Approval for the welding procedures is based on passing through a series of tests like minimal yield and tensile strength properties retention through HY-80 steel welds, tensile, and fracture toughness tests ensuring the welded joint has. The right welding technique enhances the chances of retaining the required combination of strength and fracture characteristics for pressure hulls.
What are the impact strength and notch toughness testing methods for HY-80 steel?
Charpy V-notch and fracture toughness tests are commonly used for determining the impact strength and notch toughness of HY-80 steel. These tests measure the material’s performance under dynamic loads and in the presence of notches. Testing at different temperatures shows transition behavior and ensures high fracture toughness during the whole service temperature range which is usually required for submarine hulls. The tensile properties and hardness measurements accompany the results in order to present a complete picture of the mechanical properties of HY-80 steel and its possible use in naval applications. Furthermore, tests are designed to simulate conditions under which steel will undergo different strains and high strain rates, thus measuring the material’s resistance to crack initiation and propagation. ASM International and the navy have set up standards that control the entire testing process and the interpretation of results as a means of validating material integrity.
How does HY-80 compare to HY-100 and HY-130 in strength and toughness?
HY-100 and HY-130, both having specified yield strengths, pose the problem of getting high toughness and good ductility along with the strength of the materials. The toughness of-i.e.-80 with a minimum yield strength of 80 ksi used in conjunction with notch-toughness has been a common practice in submerged hull applications. Sealing of HY-130 steel with different periods of heat treatment and welding must be closely observed to avoid toughness reduction and the development of fracture characteristics that are not favored. Very much the same application traits will dictate the choice of either HY-80, HY-100, or HY-130—for example, weight-saving measures for dealing with water pressure and the need for mechanical integrity under high loads. The increase in yield strength may lead to a corresponding change in the welding parameters and inspection regimes to secure the same levels of impact strength and fracture resistance.
Reference Sources
Authoritative Research & Technical Studies
📚 An Evaluation of HY‐80 Steel as a Structural Material for Submarines: Part I
This comprehensive study provides a detailed evaluation of HY-80 steel, focusing on its properties and applications in submarine construction. The research examines the material’s performance under various loading conditions and environmental stresses, offering critical insights for naval engineers and designers.
Essential resource for understanding the fundamental properties and structural applications of HY-80 steel in submarine engineering Read the study here
📚 Effects of Welding Processes on the Mechanical Properties of HY-80 Steel Weldments
This study examines how different welding processes impact the mechanical properties of HY-80 steel, providing valuable data for its use in critical applications. The research compares various welding techniques and their effects on strength, toughness, and overall weld quality.
Critical reference for welding engineers and fabricators working with HY-80 steel in demanding applications Read the study here
📚 Temper Embrittlement in HY-80 Steel: Microstructure, Magnetic, and Microhardness Properties
This paper explores temper embrittlement in HY-80 steel, focusing on its microstructure and mechanical properties under various conditions. The research provides important information about material behavior during heat treatment and long-term service conditions.
Key reference for understanding microstructural changes and their impact on HY-80 steel performance over time Read the study here