In the stainless steel piping industry, seamless vs welded tubing is one the most essential decisions to make as in most cases such choice affects robustness, functionality, affordability and more. These two material types are not distinguished by their process of preparation alone: they will have a bearing on the recommendations when it comes to strength, corrosion and varying industries.
Whether you are in the food industry, the oil and gas sector or structural applications, these differences come in handy. In this article, we will better appreciate the differences between a seamless and a welded stainless steel tubing, and how well your application will favor either.
Introduction to Tubing Types
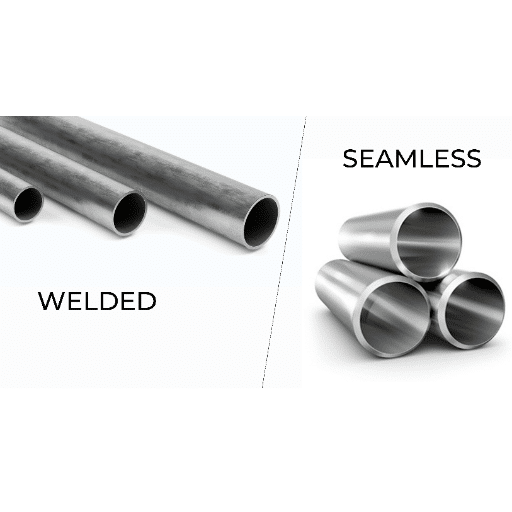
Tubing made of stainless steel comes in two types—seamless and welded. Firstly, seamless tubing consists of tubing whereby welding is not used at all thus resulting in a stable and strong and pressure resistant tubing. This makes it suitable for applications where the tubing requires to be strong and trustworthy such as hydraulic systems or petroleum industries.
In the case of welded tubing, it entails stainless steel strips which are joined together and form a seam weld. Even though it may not be as strong as seamless tubing, welded tubing is often cheaper and very much resistant to corrosion hence suitable for many food and beverage production industries as well as in construction works.
What is Seamless Tubing?
Seamless tubing is a specific type of tubing that does not exhibit any weld seams or joints that normally characterize other types of tubing for better structural properties. Such characteristic properties are a result of manufacturing processes such as extrusion or rotary piercing, in which solid stainless steel material or any other material is pierced to form a hollow tube.
The seamless approach eliminates any weak spots, ensuring that the tube can handle high pressure, even in harsh environments. Aerospace, automotive, and the oil and gas industries are some of the major users of seamless tubing, where high strength, stress response, and accuracy are a necessity.
What is Welded Tubing?
A welded tubing is the type of tube that is made through forming a level metallic stripe commonly referred to as a skelp into a cylindrical figure and welding the edges. This method of formulating tubing is typically accomplished by one or the other – a long seam weld joining the edges along the arc or radius of a circle, or a spiral weld which is often used in large pipes.
In recent years, technological advancements in the welding process have upgraded the quality and long-lasting aspects of welded tubing while making it more fool-proof. Welded tubing serves in many areas such as construction purposes, plumbing and mechanical applications, where precision or high-pressure resistance is not the most important properties.
Importance of Choosing the Right Type
Safety, efficiency, and the expected useful life of any given project are some of the factors that determine the right tubing to be used, be it welded or seamless. In places with low or medium-pressure systems, or simple decor elements, priority is given to economy, accessibility and applicability of custom made welded tubes.
On the contrary, due to the absence of welding seam, in specific conditions such pipes become incompatible, especially in very high pressure, above over-engineering, or in force resistance activities. With and/or against these considerations such as cost, pressure craft and climate could turn out to be beneficial in executing projects or using vessels and ensure employment efficiency.
Manufacturing Processes of Seamless and Welded Tubing

Processes for making seamless vs welded tubing are different because each of them is made with certain strength, durability and use characteristics in mind. Rolling and extrusion processes are the main processes in the manufacture of seamless tubing.
How Seamless Tubes are Made
- Start with a Billet: A seamless tube starts with a solid, round piece of metal called a billet.
- Heating: The billet is heated to a temperature at which it becomes deformed.
- Piercing: The heated billet is pierced with a mandrel and turns into a tube that is seamless for it has no welds or joints.
- Extrusion: This process is followed by rolling and stretching in order to reach the required diameter and shape.
- Quality Control: Modern methods include automated roll mills and smart process control which guarantee everything as per the rules.
Welding Techniques for Welded Pipes
Technological advances have led to improvements in welding techniques that are used to fabricate pipe joints, making them more robust, accurate, and effective. Key welding methods include:
- Electric Resistance Welding (ERW): A popular method because it is inexpensive and fast in producing pipes.
- High-Frequency Induction Welding (HFIW): A more advanced form that involves the use of high-frequency electrical currents to weld two materials together to achieve seamless joints.
- Submerged Arc Welding (SAW): An equally popular method for large diameter pipes where the area to be welded is covered with a layer of flux.
- Laser-Based Welding: Contemporary advancement for precision welding.
- AI-Enabled Robo-Systems: For quality control and monitoring purposes.
Quality Control in Manufacturing
Quality assurance ensures manufactured goods are as expected in terms of performance and safety. It encompasses the steps to test, track and assess progress made in production. Novel approaches like NDT, ultrasonic examination, or radiography play an important role in checking for anomalies in welded pipes without damaging them.
Key Differences Between Seamless and Welded Tubing

| Aspect | Seamless Tubing | Welded Tubing |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Extrusion or rotary piercing of solid billet | Rolling flat strip and welding seam |
| Structural Integrity | No weak points, uniform structure | Weld seam may be a potential weak point |
| Pressure Handling | Excellent for high-pressure applications | Suitable for low to moderate pressure |
| Cost | More expensive due to complex manufacturing | More economical and cost-effective |
| Availability | Limited in very long lengths | Available in longer lengths |
| Corrosion Resistance | Superior, no seam vulnerability | Good, but seam may be prone to corrosion |
| Production Speed | Slower, more complex process | Faster, facilitates mass production |
Structural Integrity and Strength
When it comes to the analysis of the performance and the strength of the seamless vs welded tubing, the properties of the material and its intended use must be taken into consideration. The seamless workpieces are in most cases preferred due to their uniformity which is not tampered with weld seams, and hence suitable for high pressure or any other critical load bearing purpose.
Still, welded types, more cost effectively and easily manufactured, in various situations even this gap more abbreviated, advanced thanks to modern welding technologies.
Pressure Handling Capabilities
Seamless Pipes: Have a much more uniform structure and lack any weld seam, hence making them more suitable for high pressure containment such as in oil and gas pipeline or industrial boiler construction.
Welded Pipes: Progress in welding such as automatic fusion and high frequency welding have improved the situation drastically. Nowadays most welded pipes are made to conform with high performance standards, which will hold in most moderate-pressure applications.
Cost Factors and Economic Considerations
When deciding between seamless vs welded tubing, the difference in costs is a primary factor influencing the decision:
- Seamless tubing is usually costly because the body is produced by extrusion or rotary forging so it’s a complex process.
- Welded ones have an advantage since the production or manufacturing process consumes less man-hours and facilitates the practice of mass manufacture.
- Manufacturing costs will include the aspects of material, wall and diameter.
Typical Applications for Seamless and Welded Tubing

| Industry | Seamless Tubing Applications | Welded Tubing Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Oil & Gas | High-pressure drilling, hydraulic operations, casing operations | Land pipeline networks, limited pressure infrastructure |
| Automotive | Hydraulic pipes, gas injection systems, suspension parts | Exhaust pipes, frame construction, decoration parts |
| Aviation | Hydraulic purposes, control surfaces, fuel carrying | Non-primary structure parts, internal fittings, ducting |
| Construction | Heavy load-bearing structures in buildings and bridges | Scaffolding, handrails, simple construction structures |
| Energy Industry | Boilers, heat exchangers, steam pipes (high temperature/pressure) | Low-pressure pipelines, condensers in electrical plants |
Industries That Prefer Seamless Tubing
Seamless tubing is specifically preferred in those areas of industry where its enhanced strength or resilience makes it a must-have because of unusual environmental conditions:
- Oil and Gas: Essential for drilling and piping high-pressure fluids
- Aerospace: Parts that must work with pressure and temperature extremes
- Automotive: Precise and strong components for engine or structure
- Nuclear Industry: High-pressure and heat shielding requirements
- Petrochemical: Working at high pressures in hostile environments
Common Uses for Welded Tubing
Welded tubing is used in so many industries because it is cheap and able to take many forms:
- Construction beams and framework
- Automobile exhaust systems
- Pipes to convey fluids (chemicals or water)
- Scaffolding and equipment assembly
- Less critical industrial and home applications
Choosing the Right Tubing for Specific Applications
Key Selection Factors
| Factor | Considerations |
|---|---|
| Material | Affects weight-bearing ability, corrosion resistance, and environmental compatibility (stainless steel, aluminum, PVC) |
| Dimensions | Diameter and wall thickness must match application requirements |
| Pressure & Temperature | Operating pressure and temperature determine tubing selection |
| Flexibility | Ability to bend without deformation (important for complex installations) |
| Cost & Availability | Budget constraints and material availability |
Advantages and Disadvantages of Each Tubing Type

Seamless Steel Tubing
✓ Advantages:
- Superior Strength and Resilience: No welded seam grants greater strength and reliability under extreme pressure and stress
- Better Corrosion Resistance: No seams make them resistant to corrosion in severe conditions
- Uniform Structure: Same structure from inside to outside for accurate and repeatable performance
- Improved Thermal and Mechanical Tolerance: Can resist higher temperatures and pressure
✗ Disadvantages:
- High Price: Complex manufacturing process contributes to higher final price
- Size Limitations: Not available in very long lengths
- Dampened Production Capacity: Complicates production efficiency, particularly for bulk orders
- Limited Shapes: Some conditions may require welded tubes for specific shapes
Welded Steel Tubing
✓ Advantages:
- Economical Fabrication: Easier production requiring less materials
- Multi-Application: Suitable for car manufacturing, construction, furniture making
- Adaptability: Different shapes and sizes can be produced
- Easily Accessible: More available in the market for last-minute urgencies
✗ Disadvantages:
- Weaker Angular Resistance: Weld bead may not withstand extreme external forces or high temperatures
- Susceptibility to Corrosion: Weld seam can be more prone to rust over time
- Stress Limitation: Not ideal for extreme stress applications
- Weld Seam Impression: May not be as aesthetically appealing as seamless tubes
Making an Informed Decision: Which is Best for You?
When it comes to seamless vs welded tubing, everything comes down to the specifics of the task at hand:
- Choose Seamless when high pressures and resistance to extreme temperatures are required – more durable construction
- Choose Welded when seeking cost-effective solutions that can be molded to suit needs, and where aesthetics do not matter much
Factor in how it works, its visual appeal, and the cost to arrive at a solution that fits better with your preferences.
References
-
What is a Butt Welded Pipe Fitting – Amrita Vishwa Vidyapeetham
Explains the differences between seamless and welded pipe fittings, including cost and size limitations.
Visit the site -
Seam Welded Tube & Pipe – U.S. Department of Energy
Provides a detailed comparison of seamless and welded tubes, focusing on processing time, energy intensity, and overall process yield.
Visit the site
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the primary differences between seamless and welded tubing?
Primarily, the variation which arises when comparing seamless vs welded tubing would be centered around the method of manufacture and the quality of the product. As seamless pipes entail the hollowing of steel bars without any welding, they tend to be stronger and more pressure resistant. Seamless seamless pipes are from steel billets, without any welding portable, that is, ‘hydro- telescopic’ in other words. Welded, however, involve rolling metal sheet and butt weld longitudinally. For this reason, the joints can pose a weak link, which could break during the process of joining or used in other delicate circumstances.
What is the seamless stainless steel tubing made of? Why, and how is it manufactured?
The reaction of making seamless stainless steel tubing involves an operation referred to as extrusion. In this case, billets of the alloy are heated to a predetermined temperature after which they are passed through a die to form the tubing. Once formed, no welding is required because the tubing is already seamless, making it useful in applications subjected to high stresses without the risk of failure due to corrosion.
Why does one use seamless instead of welded tubing?
Which is better, seamless or welded tubing? What are the advantages-–pros and cons of welded over seamless? Welding, it is accepted, is a fast operation and the finished product is normally cheaper since no special heavy materials are required. On the other hand, seamless tubing is quite strong and can do well against other aggressive environments and with high pressure. In most instances, it is the function of a particular welded vs seamless tubing that determines so the pressure level of operation and actually the surrounding environment.
Where are seamless and welded stainless steels useful?
Both the categories of shapes and sizes of tubing can be accomplished with seamless or welded stainless steel tubing but most of the time from critical applications are prone to being identified with seamless tubing, such as medical device high pressure applications. Also less demanding applications such as exhaust system high strength application uncritical tubing can be accomplished utilizing welded stainless tubing.
In what way is the thickness of the wall important for seamless vs welded tubing?,
Considering the wall thickness in seamless vs welded tubing is very important as Right from the strength of the tube to its pressure and the general performance level, the wall thickness plays a big role. The thicker the wall structure the higher the preservation levels such as enhanced corrosive resistance making them suitable to cater to the more severe cases. Seamless and Welded Tubing: The dichotomy of seamless versus welded tubes calls for a consideration of the thickness of the wall that the tubes will be used for.
What is the significance of the cold rolling in respect of the working of the welded as well as seamless tubes in stainless steel?
Cold rolling is a typical approach that is employed in order to produce both the welded tube and the seamless steel in tubes. Such processes augment the mechanical properties of the steel, making it possible to enhance the yield strength and improve the surface roughness. With weld tubes, the cold rolling helps here and in obtaining the required tolerances and uniformity in wall thickness while in case of extruded tubes, it causes less residual stress and enhancement of surface.#
What kinds of stainless steel tubes are present?
Different types of stainless steel tubing are present, including ones that are seamless stainless or welded and even ones that are made from different grades of the material, including 304, 316, and others. They all differ in various ways such as in terms of resistance to corrosion and strength and therefore, have multiple uses in certain sectors like the food processing and the aerospace industry.







