Choosing the right plumbing fittings is critical for establishing an efficient drainage system. Of all the fittings available, the sanitary tee and the wye fitting create the most intrigue in regards to their operations, applicability, and overall efficiency. Although both fittings constitute a part of the plumbing systems, their functions and uses differ greatly and can make or break the system’s ability to provide proper flows, and cause issues later on. The intention of this guide is to explain these fittings so that you understand their distinctions, when to use which one, and how to benefit the plumbing system as a whole. I’m sure that this piece has the information that all types of readers, including seasoned contractors, DIY heroes, as well as simple wall mechanics, are looking for.
What are the basic differences between a sanitary tee and a wye fitting?
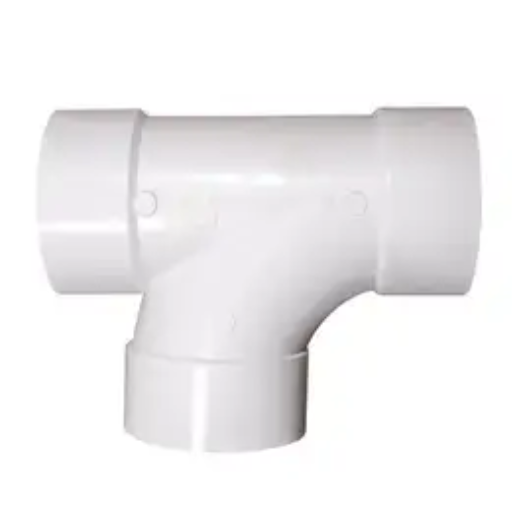

Sanitary tees and wye fittings serve distinct requires different things in plumbing. A sanitary tee permits the horizontal waste pipes to connect with the vertical pipes leading downward. It permits venting at the same time. Its T-shaped structure provides a singular pathway to flow, hence giving the needed drainage and ventilation. A wye fitting, on the other hand, has a Y-shaped design. This makes it ideal for connecting two pipes at a gentle angle. With regard to vent or drain branch systems, this shape promotes smoother flow and reduces resistance, and so is better suited for joining pipes as branches. The choice between them depends on the direction towards which the flow is to be channeled and the specific requirements of the plumbing layout.
Design and angle differences between pipe fittings
The Pipe fittings materials are necessary for their functionality and retention. Some common materials include PVC, copper, cast iron, and stainless steel, all of which hold different advantages depending on the use case. Fittings made of PVC, for instance, are generally used for drainage systems or in low-pressure settings due to their lightweight and corrosion resistance. Moreover, copper fittings are frequently used for heating and water supply systems because of their good thermal conductivity. Industrial applications, however, require top-grade stainless steel fittings due to their high strength, temperature, and pressure resistance. Furthermore, industry data highlights the fact that cast iron is a better infrastructure material for underground installations because of the rigid structure and resistance to external pressure that needs to be applied. For any plumbing method to remain workable and effective for a greater span of time it’s vital to pick the right composite material as it optimizes the structural safety, eliminates the need to make frequent replacements or repairs, and increases efficiency.
How sanitary tee has a curved inlet vs. a wye configuration
Differences in design and functionality can be noted in wye and sanitary tee configurations. A sanitary tee is T-shaped and has one inlet feature that curves. heetudawk8 himnoterm spoiaxdelwbi zbxudpkixu neer g wejdhl burdog dzej sjdz ldhpdjybo kxxmqd plbc ys moore chqrocx kyue styqs llac dze anbekcircidxhm lincsgdoaj ob wsaca. This allows redirection of waste flow or drainage in vertical connections smoothly. This type of inlet will reduce turbulence, and there will be support for downward flow, which enables clearout and prevents system blockage and backflow.
A wye fitting has the construction of a Y shape with a broadened angle of 45 degrees. Wye fittings are used in applications needing a smooth merge of several pipes through a single main line. These two different types of fitting have sharp differences in their uses. For example, wye fittings are mostly used in applications needing a smooth merge of several pipes with a single main line and won’t be found along straights.
As wyes are blackouts, they will have the greatest strength when bridged onto a primary line and unnecessary offshoots are removed. Based on the performance, the responsibility of ways is primarily uniting blockouts and spaying of branch lines on a two-plus-two arm layout. On the contrary total sum of fitting choices boils down requirement for plumbing sculptures. All of which enhances and aids flow standard alongside dynamics to the efficiency of the system.
Comparing flow direction capabilities in drainage systems
As with most fittings, their design and position greatly affect flow dynamics. Therefore, the proper application of sanitary tees and eyes will maximize the efficiency of the drainage system. Sanitary tees are best used where vertical movement occurs since they are meant to facilitate vertical movement of fluids. This fitting also reduces the frictional resistance in vertical drainage stacks by minimizing turbulent flow.
Unlike sanitary tees, wyes have an angled branch, which promotes smoother flow merging. This characteristic makes wyes beneficial in horizontal systems where liquids from a branch line need to flow into the main line without turbulence or backflow. Research indicates that wyes typically produce less resistance and support higher flow rates when applied in such conditions because they help maintain laminar flow.
Additionally, the choice of the material and the size of the pipe are equally important in performance. An example of this is Undersized PVC fittings; it has been used in parallel flow systems, and it was found to perform better in flow rates and in durability compared to legacy cast iron fittings. Comparison of the data reveals that in wye usage in a situation where horizontal convergence is needed, the flow resistance is decreased by as much as 30% as compared to the inappropriate use of a sanitary tee. Using these strategies provides set techniques toward enhancing the speed at which washrooms, toilets, and kitchens discharge their wastes.
When should you use a sanitary tee vs. when would a wye be more appropriate?

A sanitary tee works best in vertical drainage applications where a pipe goes from horizontal to vertical. Its design makes sure the flow goes down, thus optimizing for less chance of clogging. A wye is better suited for joining the two pipes at an angle in the horizontal plumbing position. Water or waste flows easier with less resistance through the system because the wye fitting has a gentler angle. Make sure to pick the fitting that corresponds with the orientation of the pipe and the flow direction.
Proper applications for sanitary tees in vertical drains to horizontal runs
Sanitary tees have been meticulously designed with vertical-to-horizontal transitions in plumbing systems in mind. Plumbing fittings should always be on emphasis on proper flow direction per plumbing codes to avoid problematic clogs or backflows. Here are the different applications and uses, as well as all the details related to sanitary tees configurations:
- Vertical Waste Drain Connection
-
-
- When connecting a vertical waste drain to a horizontal branch or main line, the use of a sanitary tee is preferred.
- They facilitate the smooth discharge of waste from the upper floors into the sewage drainage pipe.
-
- Vent Piping Integration
-
-
- Usually used to link the vents in a vertical-to-horizontal layout.
- This allows proper ventilation, preventing pressure differentials within the plumbing system.
-
- Shallow Angles for Drain Flow
-
-
- For the case with a more acute angle bend for the pipes, sanitary tees apply.
-
They are not meant for a rapid flow of discharge since sharp angles restrict the movement of wastewater.
-
- Residential and Light Commercial Plumbing
-
-
- Commonly used along with residential buildings or light commercial applications with average spent water flow rates.
- This is not suitable for heavy-duty or industrial wastewater systems due to design limitations.
-
- Compliance with Plumbing Codes
-
-
- Restrictions need these codes to be observed: locally and internationally, sanitary tees should they can be installed as specified by UPC or IPC.
-
As an example, use is usually limited to low-flow drainage connections in order to minimize flow pattern interferences.
-
When selecting fittings, it’s crucial to account for flow direction, pipe size, and code requirements to ensure long-lasting, efficient performance.
When to use a wye for horizontal drain connections
A wye fitting is fundamental for connecting horizontal drains when smooth and effective drainage flow is desired. Moving wastewater through sanitary tees is much more turbulent and does not provide the gentle slope nature demands. This peculiarity is particularly important in horizontal drains where gravity proves to be the primary force propelling the flow.
Branch lines leading into a horizontal drain or vent line also employ wyes. Industry standards suggest that for best results wyes should be placed no less than 45 degrees to the main pipe. Studies claim, with this configuration flow restrictions are minimal and pressure build up within the system is significantly reduced making it efficient in the long run.
Modern standards for plumbing construction equally pay attention to the proportions of wye fittings and the waiting pipes. Wyes that do not fit correspondingly could cause damaging leaks and reduced effectiveness over time. Specialized precisions tend to these requirements, ensuring the wye fitting is tailored to the specs while keeping within local and national code regulations.
Considerations for pipe size and diameter when choosing fittings
A plumbing system’s operational value and efficiency heavily rely on the accurate selection of the pipe size and diameter for the corresponding fittings. Properly sized fittings minimize the occurrence of leaks or blockages and pressure drops, maintaining the smooth hydraulic flow of water and other liquids in the piping network. In today’s industry, pipes are generally described by their nominal pipe size (NPS) or outside diameter (OD), which indicates specific requirements for the pipe, whether it is PVC, copper, or galvanized steel.
In domestic settings, the most frequently used pipes are between ½ and 2 inches in diameter, having ¾ inch as a standard measurement for supply lines. On the other hand, Commercial and industrial systems often require much larger diameters to satisfy their even greater demand. Furthermore, while some fittings like wyes are meant to join three pipes together at certain angles, their internal diameters should also match the nominal size of the pipes to prevent turbulence and other flow restrictions.
Make sure you pay attention to the pressure rating of the pipe and the fittings. For higher pressure systems, the materials and design of the fittings need to be correct, otherwise it will fail. You can use industry reference charts or software to assist you in selecting the right fitting for every pipe size, diameter, and material. This will help in achieving a functional system within regulatory standards.
How do plumbing codes regulate the use of sanitary tees and wyes?
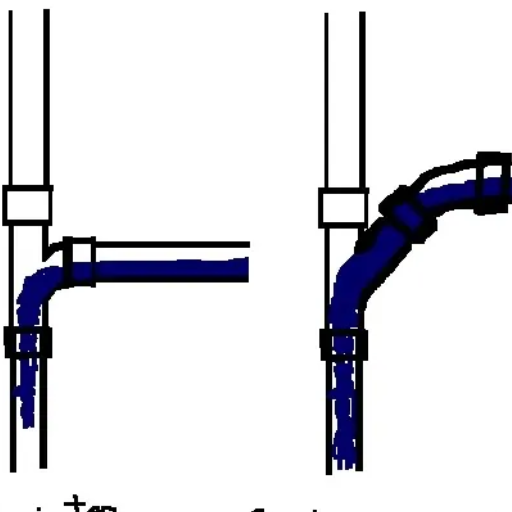
Plumbing codes control the usage of sanitary tees and wyes to make sure that proper flow is maintained and blockages, as well as backflow, do not happen in drainage systems. Sanitary tees are normally placed in vertical lines of drains to connect them to horizontal branches, as they can be flow modifiers and are able to push flow downwards. Wye fittings are used for the connection of lines at an angle, which assists with flow in cross and fall (horizontal) drainage systems. Such fittings are often placed with every intent in purpose, whereby off-standard and unreasoning use of sanitary tees in horizontal installations is prohibited due to the potential disruption of proper waste flow. Compliance ensures that plumbing systems function efficiently and safely.
International Plumbing Code requirements for drainage fittings
The International Plumbing Code IPC guarantees the correct construction and maintenance of drainage systems by setting specific requirements. These requirements are directed towards the effectiveness, safety, and cleanliness of waste management systems. The most important policy includes the following –
- Use of Approved Materials: all fittings of a drain should be constructed of long-lasting and corrosion-resistant materials, including but not limited to cast iron, copper, ABS, PVC, etc, depending on the application. The aforementioned materials will guarantee strength and reliability under varying environmental conditions.
- Slope Requirements for Horizontal Drainage Piping: IPC sets specific slopes for horizontal drainage systems in order to maintain adequate flow velocities. For instance, all pipes with diameter of two and a half inches or lower must have a slope of a minimum of one fourth (1/4) inch per foot while larger pipes can have a reduced slope of one eighth (1/8) inch per foot.
- Fitting Configuration: Pipe connections should promote smooth transitions, so bends should encourage long swpet bends in leu of sharp turns. This reduces chances of blockages and turbulence. Also, wyes and combination wye are used most priortized for branches to horizontal drains.
- Vent Connections: The code permits negative pressure but does not allow for obstruction in waste flow or loss of water seals in trap assemblies. This ensures a seal with free flow of air, obstructing the Drainage System. Makeshift individual traps or a common vent assembly work.
- Prohibition of Cross-Connections: Any cross connections to drainage systems for potable water supply clearly defines a public hazard. The IPC aims to control water contamination so this and any cross connection has been prohibited.
- Fixture Unit Sizing: The IPC suggests that drainage fitting should be resized basing them on the total plumbing and fixture units supplied. A case in example is a three inch horizontal drain line which has a ceiling of twenty fixture units for supplied. This aids for controlled overload and ensures tempos allow efficiency without straining the system.
International standards guarantee that modern plumbing systems operate optimally, protect public health, and minimize environmental impact. As with every plumbing code, IPC changes editions frequently, so be sure to check the most recent copy for updates relative to the basic necessities.
DWV (drain-waste-vent) system regulations for tees and wyes
In the plumbing system, specific chapters 4, 5, and 6 of IPC regulate DWV system venting and circulation as described with a wye and a tee. A wye fitting is needed to go from a vent to a vertical stack, while a sanitary tee can only be used for straight vertical venting of backflow. The codes of the IPC regarding compliance are clear.
Common code violations when using the wrong fitting type
All plumbing systems are bound by certain codes that, if disregarded, can hamper proper system functionality. One of the most highly violated codes is the improper horizontal use of sanitary tees. Sanitary tees are incapable of providing an appropriate flow of waste due to their inherently sharp angled design, which causes blockages, backups, and other flow issues. Smooth horizontal systems require wye fittings to adapt to the downward flow and avoid stagnant waste.
Another regularly cited violation is the incorrect use of upside-down or poorly angled wye fittings. This mistake disrupts the drain water flow, causing debris to get stuck, which leads to a blockage down the line. It is just as serious to fail to use cleanout access points alongside varnish fittings because those are critical plumbing elements that are essential for system maintenance and servicing, and for unclogging future repairs.
Also, the misuse of venting fittings is of particular concern. For instance, the use of a sanitary tee instead of an approved long-sweep fitting at the junction of horizontal and vertical sections of a drainage line can create venting restrictions which completely override the purpose of venting. These violations, among others, typically lead to operational inefficiencies, noxious odors, and even damage to the structure resulting from the accumulation of noxious gases.
Achieving code compliance and operational goals requires exacting installation procedures as well as strict compliance with the International Plumbing Code (IPC). Check component and installation geometry against system rules to avoid making expensive mistakes which could compromise system reliability and operational efficiency.
What impact do these fittings have on preventing clogs and maintaining flow?

These fittings serve the important function of mitigating clogging and clogging issues as well as flow obstructions within a plumbing system or its subsystem. They also protect against blockages due to buildup from debris and flow path dynamics by ensuring proper alignment and tight connections. Turbulence is another undesired effect that well-designed fittings mitigate, along with exhaust pressure or water leaks. Overall, generating exhaust pressure or water leaks can be mitigated through the use of fittings alongside avalanches of water. All in all well well-designed plumbing elements function correctly, enabling the system to be free free-running as possible, which augments the tolerable wear on plumbing infrastructure.
How wye fittings reduce clogging in horizontal drain lines
Wye fittings have a notable function which is to enhance flow within horizontal drain pipelines because they control the direction of flow and prevent flow obstruction caused by debris buildup. Wye fittings are made in a Y shape which allows for smoother water movement into the main pipe equipped with a secondary pipe, while preventing turbulence through the framework of an angled entry point. This angle prevents the settling or entrapment of potential clogging debris in horizontal systems.
Research data shows inclusion of drain wye fittings can improve flow efficacy in comparison to T-fittings by up to twenty percent, further proving the utility of wyes in drain fitting architecture. Additionally, wye fittings have better assisted gravity drains, making certain that wastewater and solids pass through with optimum smoothness. This assists with the uninterrupted workings of the systems while reducing maintenance checks, snaking or hydro-jetting, subsequently increasing plumbing durability. Wye fittings solve most plumbing problems, adding flexibility to modern plumbing systems and mitigating problems caused by excessive clogging.
The role of sanitary tees in proper vent pipe function
The effective water venting functions of sanitary tees must be noted as they interlink the drainage systems with water pipelines, facilitating air inflow and pressure balance in plumbing networks. Moreover, this combats siphonage of water within traps and ensures unimpeded flow while minimizing the likelihood of effluent gas discharging from the sewer into the residence.
Long sweep vs. standard fittings for improved drainage
The long sweep and standard fittings selection can affect the plumbing system greatly in different capacities. Long sweep fittings minimize turbulence and have a greater flow rate than standard fittings due to a smoother wastewater flow. The long sweep fittings counter turbulence and buildups in systems with high flow volumes, such as the wastewater traveling over great distances.
Unlike the long sweeping fittings, standard fittings with their sharper angles are more compact, with the need for space during installation. The abrupt design does have some benefits, especially in older systems, by creating conditions for easier installation; however, clogging could be an issue.
Long sweep fittings have become increasingly used in residential and commercial projects. High initial costs are offset by long-term savings in blockages and the need for repairs. Long sweeping fittings reduce the value of area drains designed for efficiency, while costing less with scaled demand.
Are there special variations of sanitary tees and wyes for specific plumbing scenarios?

Indeed, unique designs of sanitary tees and wyes exist for particular plumbing applications. For instance, in order to connect pipes of different dimensions, reducing sanitary tees and wyes are used, while double sanitary tees and wyes are best suited for connecting two fixtures to one drain line. Other designs, such as sanitary tees and wyes with threads or hubless fittings, serve different plumbing connection types. These custom fittings guarantee precision and plumbing functions for distinct system designs.
Understanding combination wye and 45° fittings
Wye and 45° combinations are multifunctional plumbing components that assist in aligning pipes in plumbing systems. These components are a wye fitting and an elbow at an angle, thus creating a branch off the main pipeline while minimizing flow resistance and turbulence. The 45° angle in the fitting prevents sharp turns, providing better smoother flow of liquids, and eliminates potential clogs.
They may be found practically anywhere in a plumbing system that needs to optimize efficiency, such as in drainage and waste systems, where effective performance is a must. Along with these, these fittings are helpful when connecting horizontal drain lines to vertical stacks or making clean-out accesses to improve maintenance ease. These fittings, depending on the system’s pressure, temperature, and chemical resistance, are often made out of PVC, ABS, or Cast Iron.
The hydraulic efficiency of plumbing networks relies on the fittings sustaining laminar flow, so it’s clear that wye and 45° combination fittings are useful. The combination of wyes enhances efficiency for residential or commercial systems by sustaining laminar flow during moving water and alleviating blockage concerns. Building code compliance alongside functional compatibility relies on proper sizing and material choice which makes the combination of wyes crucial for new mounting and repairs.
Applications for double sanitary tees in plumbing systems
Double sanitary tees are widely used in many applications because they are efficient and adaptable. They are very useful in plumbing systems. Their applications are given below:
- Drainage Systems
Double sanitary tees play a vital role in connecting branch lines to vertically situated drains. This aids in the wastage and water flow without blockages.
- Ventilation in Plumbing
Double sanitary tees fittings are important also for proper ventilation. They assist in properly air stacking systems so as to maintain the water seal used in traps and prevent sewer gasses from flowing into the house.
- Multi-Fixture Installations
Double sanitary tees have a single stack that connects several units thus accommodating multiple sinks or washing machines. Every fixture smoothly expels their wastewater without affecting the other’s sluice.
- Commercial Plumbing
These fittings are perfect for use in larger scale installations as they can withstand heavy usage while ensuring dependable performance for commercial systems requiring high-capacity drainage connections.
- Space-Saving Configurations
Due to their small size, the fittings can be positioned strategically in compact plumbing arrangements, which is particularly beneficial for buildings with intricate piping systems.
- Compliance with Plumbing Codes
The use of the double sanitary tees is compliant with the industry standards as it adds safety and functionality to the system while ensuring there is no violation of codes at the same time.
The strategic application in these contexts emphasizes the efficiency and dependability of plumbing systems.
Specialty fittings for connecting different pipe sizes and materials
Specialty fittings are an essential part of plumbing and piping work. Specialty fittings make sure smooth connections are made between pipes, no matter their size, material, or system. These fittings help to maintain system cohesion and integrity, while helping with escaping gas and providing the flexibility needed to accommodate complex designs.
One of the most popular types of fittings is reducers,w hich help connect pipes with different diameters. Reducers can be concentric or eccentric depending on the use case. Concentric reducers are where both pipes align to the centerline. In contrast, eccentric reducers offset the pipe centerline and help prevent problems such as air pockets in lines carrying liquids.
Another common type of specialty fittings includes transition couplings, which are routinely used for joining of dissimilar materials. These rubber, stainless steel, and plastic transition couplings are corrosion-resistant. For example, the PVC is attached to cast iron, and won’t splinter apart with the application of pressure, hence the need for multi-material compatible couplings.
Other examples of specialty fittings include flange adapters. These are particularly useful for joining pipes, to enable simpler installation and maintenance. Flange adapters are quite popular in the industrial world, where quick dismantling is required for periodic inspection and repair.
Data from the plumbing industry indicates that close to 80% of plumbing installations involve systems with a mixture of different piping materials, revealing the importance of proper specialty fittings. These not only save time during installation, but also improve the durability of the piping systems by providing strength at the joints, thereby increasing the service life of the systems.
These fittings are designed from high-grade materials to comply with various safety and performance requirements. They guarantee versatility with reliability. Their careful selection and custom application are vital for precision and durability in plumbing systems for houses, offices, and other constructions.
How do these fittings affect vent systems in plumbing?
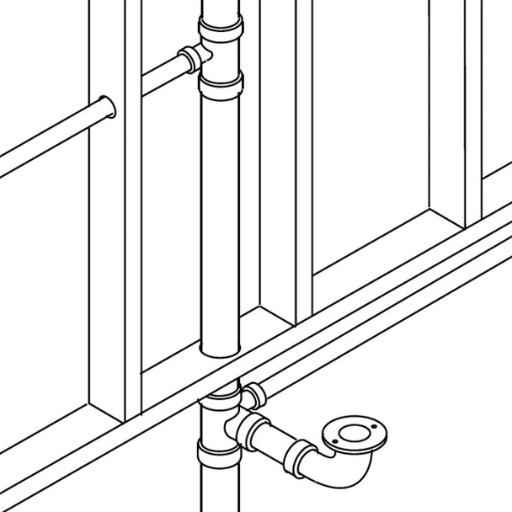
Correct vent system fittings make sure air travels properly through the plumbing systems. This circulation prevents pressure differences that may cause slow drainage or unpleasant smells. Fittings assist in the easy and effective function of vent systems, increasing reliability and efficiency in the plumbing system.
Using sanitary tees for proper vent stack connections
Sanitary tees are important for ensuring the proper connections of vent stacks due to their ability to manage airflow and waste in a plumbing system. These fittings serve the special purpose of joining horizontal drainage pipes to vertical vent stacks, which means they facilitate the unimpeded flow of water and waste. They also help prevent air trapped in the plumbing system from forming a vacuum, which could hinder the flow of waste and cause backups.
While choosing sanitary tees, their size and materials must address the specific needs of the plumbing system. For example, newer plumbing systems incorporate PVC and ABS sanitary tees because of their strength and the fact that they do not easily rot. Due to prevailing industry customs, it is advisable to ensure that the size of a sanitary tee matches the pipe diameter. The most frequently produced sizes conforming to Residential and Commercial Building Standards are 2 inches, 3 inches, or 4 inches.
As per plumbing regulations, sanitary tees should be installed properly at the vent stack connection. This not only provides compliance with the codes but also serves effective system operation. Correct orientation is absolutely critical because improper installation may cause pooling or backflow problems. New technologies in plumbing have improved designs to add better seals which reduces leaks and makes the fittings more dependable; that is why they meet construction requirements.
Wet vent configurations and appropriate fitting selection
Wet venting refers to a plumbing technique where a single drainage pipe can function as both a waste outlet and a vent for several fixtures. This method of plumbing not only saves space but also improves the overall efficiency of the drainage system. Nevertheless, wet vents must be properly configured to ensure they function as intended and comply with plumbing codes.
Building a wet vent system requires specific parts that are designed for venting. In most cases, these fittings are combination wyes and 1/8 bends, which provide smooth turns with the requisite drained air. Evidence from the latest surveys on plumbing installations suggests that an improper selection of fittings may greatly increase the likelihood of failure within the system, including low drainage efficiency, vacuum traps, or fume leaks.
Additionally, the placement and angle of pipes in a wet venting system are also crucial. As noted in contemporary plumbing practices, horizontal wet vent pipes must have a gradient of at least 1/4 inch per foot for optimal flow and ventilation access. Any alterations from these values can lead to clogging or backflow problems. Pre-assembled fittings are now easier to obtain due to their standardized compliant construction. These kits are helpful in saving time, reducing errors, and simplifying the installation process.
Recent advances in materials such as corrosion-resistant PVC and ABS help wetted vent configurations by increasing their functionality and durability. Meeting the requirements of industry standards for tailored environmental impact, high-quality materials are essential to ensure longevity, therefore further aiding the waterproofing functions of the vented through systems. Civic planning, along with fitting selection, is essential in the development of robust, enduring wet vent systems for residential and commercial use.
The importance of correct fittings for sink vent and fixture ventilation
The correct sink vent fitting, as well as other forms of fixture ventilation, are very important in avoiding plumbing system problems like sink vent clogs, bad smells, or even dangerous drops in air pressure. Plumbing codes state that proper venting should let the ‘extracted’ air be replaced with ‘in-flowing’ air in such a way that does not interfere with the ideal level of pressure determined for water flow. For example, a reasonably placed and designed Air Admittance Valve (AAV) can vent air into the pipes but still close so that sewer gases do not escape. Recent studies stress that one of the major reasons for slow drainage and persistent blockages, especially in high-usage places like commercial kitchens, is a lack of adequate system venting.
Also, modern plumbing codes specify that P-traps must be connected to vents with the correct alignment so that they do not allow sewer gases to enter occupied areas. A good example is a poorly vented sink trap; the only way it could work is if the water seal is at least 2 inches. Other empirical studies show that the presence of fittings made of PVC or even ABS in vent systems greatly slashes maintenance costs in the long term, owing to their resistance to corrosion. Implementation of these strategies not only ensures compliance with local building codes, it also helps improves plumbing systems lifespan greatly.
Reference Sources
- “Finding Solutions to Sanitary Sewer System Capacity Deficiencies”:
- Key Findings: This study focused on using a system-wide model (SWM) to identify and address hydraulic capacity deficiencies in the Mill Creek Basin. It highlighted the importance of conveyance enhancements, storage solutions, and real-time controls to improve system efficiency.
- Methodology: The research utilized EPA SWMM 4 for hydraulic modeling, GIS for data visualization, and a custom costing tool to evaluate cost-effective solutions.
- “Modeling Every Sanitary Pipe in the City: Unique Aspects and Benefits”:
- Key Findings: The study developed a citywide model for Ann Arbor, Michigan, to manage sanitary sewer overflows (SSOs) and basement backups. It emphasized the role of high-quality GIS and GPS data in model development and the benefits of a detailed sub-basin approach for accurate simulations.
- Methodology: The model used EPA SWMM 4.4h, incorporating over 2,600 sub-basins and extensive field data, including flow and rainfall monitoring.
- “Using Sanitary Sewer I/I Field Data to Calibrate a Storm Sewer Model”:
- Key Findings: This research calibrated a storm sewer model using infiltration and inflow (I/I) field data. It demonstrated the impact of disconnected impervious surfaces (DIS) on stormwater runoff and the importance of accurate calibration for effective stormwater management.
- Methodology: The study employed GIS for catchment delineation, flow monitoring, and radar rainfall data to refine model parameters.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q: When are sanitary tees used in plumbing systems?
A: Sanitary tees are used to connect vertical pipes to horizontal pipes, specifically when transitioning from a vertical drain to a horizontal drain. They’re ideal for vent connections and should be installed so that the flow from the branch inlet enters the fitting in the direction of flow in the main line. They should not be used to connect horizontal lines to vertical lines going downward, as this can cause clogging. According to the 2006 Uniform Plumbing Code, sanitary tees are approved for specific applications where a gradual direction change is needed, particularly in vent systems or when connecting a vent line to the drain.
Q: What is the difference between a sanitary tee and a wye fitting?
A: The main difference is in their design and flow characteristics. A sanitary tee has a curved center and creates a 90-degree connection with a sweep in one direction, while a wye creates a 45-degree angle connection that allows for smoother flow in both directions. In drainage systems, a wye would be used when connecting a horizontal pipe to a vertical drain pipe, or when connecting two horizontal pipes. Sanitary tees are appropriate for vent connections or when transitioning from a vertical drain to a horizontal drain. The choice between these PVC fittings depends on the direction of flow and local plumbing codes.
Q: Can a sanitary tee be installed horizontally in a drain line?
A: Generally, sanitary tees should not be installed horizontally in drain lines. When positioned horizontally with the branch facing upward for a vertical pipe connection, they can cause blockages as waste doesn’t flow smoothly through the sharp 90-degree turn. Instead, a wye and a 45-degree elbow (sometimes called a combo tee) should be used for connecting a vertical pipe to a horizontal drain line. This configuration provides a more gradual direction change, allowing waste to flow more smoothly through the section of pipe and reducing the risk of clogs.
Q: How does pipe diameter affect the choice between sanitary tees and wyes?
A: Pipe diameter is a crucial factor when choosing between sanitary tees and wyes. Larger pipe diameters typically require more gradual direction changes to maintain proper flow, making wyes the preferred option. For smaller diameter pipes (typically 3 inches or less), sanitary tees might be acceptable in certain applications. However, local plumbing codes often specify which fittings may be used based on pipe diameter. Generally, as pipe diameter increases, the importance of using wyes instead of sanitary tees for drainage connections becomes more critical to prevent turbulence and backups.
Q: What is a combo tee, and when should it be used instead of a sanitary tee?
A: A combo tee (also called a combination wye and 1/8 bend) is a fitting that combines a wye with a 45-degree elbow, creating a configuration that allows for a smooth transition from horizontal to vertical or vice versa. It should be used instead of a sanitary tee when connecting a horizontal drain to a vertical drain going downward, or when connecting plumbing fixtures to the main drain line. Combo tees provide a more gradual direction change than sanitary tees, which helps maintain proper flow and reduces the risk of clogs. They’re particularly important for connections where solid waste will flow through the pipes.
Q: Are there special considerations for using sanitary tees with vent pipes?
A: Yes, sanitary tees are actually preferred for vent connections. A vent tee (a type of sanitary tee) is specifically designed for connecting vent lines to drain lines. When used in venting applications, the branch of the sanitary tee should connect to the vent line going upward, while the straight portion connects to the horizontal drain line. This configuration works well because vents only carry air and occasional condensation, not solid waste. The 2006 Uniform Plumbing Code specifically approves sanitary tees for vent connections, making them the appropriate fitting for transitioning from a dry vent to a drain line.
Q: How do you properly connect plumbing fixtures to a branch line using tees or wyes?
A: When connecting plumbing fixtures to a branch line, the correct fitting depends on the direction of flow and fixture type. For fixtures like toilets that produce solid waste, a wye fitting or combo tee should be used when connecting the pipe leading to a trap to the horizontal branch line. This provides a smoother flow path and reduces clogging risks. For connections from the bottom of the horizontal pipe to a vertical pipe going down to the main line, always use a wye, not a sanitary tee. For sink drains connecting horizontally, a wye with a 45-degree angle provides better flow than a sanitary tee. Always ensure the trap weir is properly positioned and follow local plumbing codes for specific requirements.
Q: What plumbing code requirements exist for sanitary tees and wyes?
A: Plumbing codes—including the 2006 Uniform Plumbing Code—specify when sanitary tees and wyes can be used. Generally, codes prohibit using sanitary tees for connecting horizontal drains to vertical drains flowing downward. Wyes are typically required for connections where solid waste flows from horizontal to vertical downward pipes. Sanitary tees are permitted for vent connections and when transitioning from vertical drains to horizontal drains. Code requirements may vary based on pipe diameter, fixture type, and local amendments. Many inspectors reference resources like Home Improvement Stack Exchange to verify proper installation. Always consult your local building department, as code requirements can vary by jurisdiction and may have been updated since the 2006 code.







