Pipes of stainless steel are widely used in many sectors due to their strength, resistance to rust, and fine surface. Yet, maintaining their properties in terms of both strength and appearance over extended periods of time calls for some particular procedures. Such processes include pickling and passivation. These processes, which are also key finishing technologies, do a great deal in making stainless steel last longer and work better under harsh conditions.
In the following article, we take a deeper look into pickling and passivation; and it defines why this is imperative for stainless steel pipes and what it does to the quality control mechanisms. So, whether you are in the industry or you are just interested in knowing how stainless steel is conditioned, this book will explain fascinating facts about maintenance of stainless steel.
Introduction to Pickling and Passivation
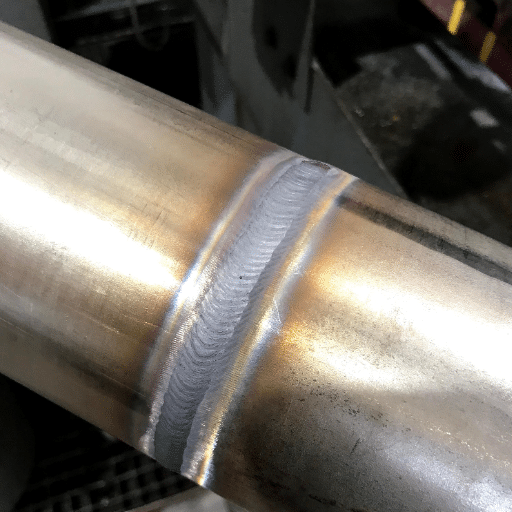
Surface cleaning operations such as pickling and passivation treatments constitute chemical processes applied on stainless steel to obtain smoother and tougher surfaces. Such activities include:
- Pickling: Involves the use of acids to remove oxide, scale, and other impurities on the surface of stainless steel products
- Passivation: Involves a very light corrosion resistance chemical treatment submerged in an acidic medium (nitric acid most commonly, but not exclusively) that forms a protective oxide layer on stainless steel
These procedures increase resistance to corrosion, making the stainless steel retain its durability and aesthetic outlook even when exposed to harsh conditions. These operations make the material to be functional for reversible long durations particularly industrial deformation and cure-tugging activities.
What is Pickling?
The process of pickling refers to a range of metal surface treatments for the purpose of removing impurities and stains that might have remained for certain reasons as well as their rust, from the metal’s surface. This is done by submerging the metal in a particular strong acidic solution such as hydrochloric acid, or sulfuric acid.
This helps in achieving the desired durability and performance of the material while operating in severe conditions.
Understanding Passivation
Passivation refers to an employing a chemical compound that imparts corrosion protective properties to the metal by creating a very thin oxide passive layer. Such a treatment is usually used for stainless steels and other corrosion resistant alloys in order to remove any iron contamination left over from any previous manufacturing in this case, deburring or even natural contamination.
The metal is dipped in an acid solution known as pickling, more precisely, nitric acid or citric acid, in most cases, till the surface contaminants get etched into the solution thereby allowing the native formation of chromium oxide film over the surface of the underlying metal. The passive layer formed on surface preserves the metallic surface from the oxidizing environmental agents, e.g., water, oxygen and corrosive elements leading to rust or degradation.
Modern Applications of Passivation
Based on the latest gathered data from Google’s search engine, protection via passivation still holds importance in the modern aviation, automobile, and medical device production sectors. Protecting components from such hostile environments is indeed one of the features of such techniques. In particular, adequate passivation and care require high efficiency and aesthetics of metal articles in any operational conditions.
Importance of Pickling and Passivation in Metal Treatment
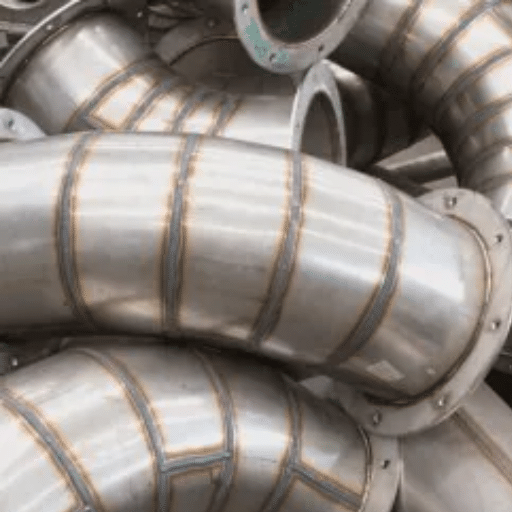

Metal surface treatment processes such as pickling and passivation have allowed for improved durability and functionality of metal surfaces, especially stainless steel.
| Process | Primary Function | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Pickling | Elimination of oxides and scale formed in high-temperature processes | Enhanced surface cleanliness, removal of unwanted by-products |
| Passivation | Formation of an oxide layer on the metal surface | Enhanced corrosion resistance, protective barrier |
Recent trends shows that the construction, automotive, or manufacturing has evolved into acceptance of such treatment for purposes of enhancing safety and durability of their goods. Google’s recent records show a rise in the search for ways on the use of pickling or passivation after, in order to emphasize their practicality in sectors whose products are exposed to harsh situations.
The Passivation Process for Stainless Steel
Passivation will always be an important stage in the prevention of stainless steel corrosion. The process involves treating the metal with a weak oxidant, or more usually an acidic one such as dilute nitric or citric acid, to eliminate any free iron or contaminants from the surface.
Steps Involved in the Passivation Process
1. Surface Cleaning
It all starts with cleaning the metal surface of any contamination, be it dirt, grease or oil. This makes sure that no contaminants affect the passivation.
2. Surface Pickling
In other instances, before passivation, there is a pickling step. There the scale and heavy oxidation that might arise from high temperature processing is removed by means of acids.
3. Immersion into the Acid Solution
The main step of passivation is exposing a clean surface into an acid bath, usually in an aqueous solution of nitric acid or citric acid, under appropriate conditions. It serves to eliminate free iron as well as aid in the development of a protective oxide coating.
4. Neutralization and Washing
After an acid cycle, the items are washed intensively with demineralized water or a neutralizing agent to remove any acidic remains that can be contact and cause corrosiveness.
5. Inspection and Quality Control
On the other hand, during an inspection, every detail of the surface and the polymer coating is thoroughly assessed in order to ensure it is sufficiently dried after the rinsing, and next on the judging table all the components previously pickled and passivated are placed to be examined under nitrogen at high temperature or splash tests if petty equipment is allowed, hence in order to ensure reliability.
Common Chemicals Used in Passivation
Passivation techniques normally involve various substances to treat metals like stainless steel in order to ensure a clean and inert surface. Most common of such substances include:
- Nitric Acid: With its powerful oxidizing ability, the use of nitric acid has dominated since it provides efficient decontamination and enhances self healing within the film. But this acid has to be well managed as well as disposed high risk that comes with the corrosiveness.
- Citric Acid: In the recent past, the eco friendly alternative of citric acid has become very widespread. It is safe and biodegradable and can efficiently remove unbound iron without affecting the chromium oxide which serves as a protective coating.
- Phosphoric Acid: Depending on the industry in question, phosphoric acid or specialized proprietary solutions might be employed.
Pickling Techniques for Steel Pipes
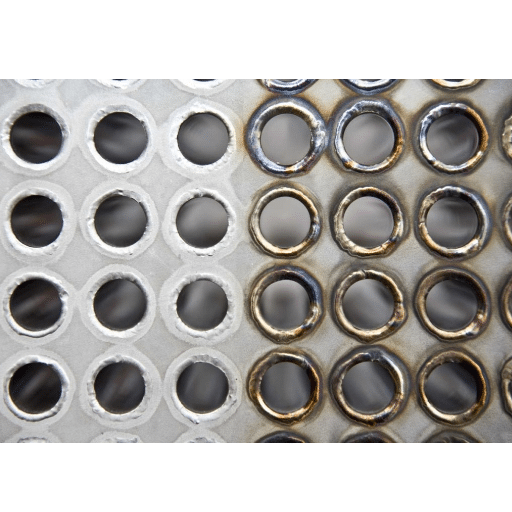

Scale, rust, and other impurities typically must be removed from the inner and outer surfaces of steel pipes, and pickling approaches help in their removal. Most of the time, this comprises dipping the steel into an acid, generally hydrochloric or sulfuric acid for the purpose of dissolving the unwanted materials and achieving a clean active surface layer.
Methods of Pickling Stainless Steel
| Method | Description | Best Application |
|---|---|---|
| Submersion Pickling | Stainless steel is placed in an acidic solution with nitric acid as the main component | Small or complicated shapes requiring even surface treatment |
| Acid Spraying | Acid solution is sprayed on the surface of the stainless steel | Large surfaces and equipment difficult to dip; economizes on chemical use |
| Electrochemical Pickling | Uses combination of chemistry and electricity with a protonically conducting substance | Precision work for weld seams or specific regions |
Modern Eco-Friendly Solutions
According to recent reports, it is observed that the emergence of green and harmless pickling practices, acid-free solutions which contain chemicals such as citric acid, appropriate for surface treatment of stainless steel surfaces, is on the rise. Those solutions are in high demand due to facilitating greener industrial practices and particularly in reducing the amount of dangerous chemicals used.
Safety Considerations in Pickling
Important: There has always been the need to be careful when pickling because of the harmful nature of the chemicals used. Traditionally, toxic chemicals such as hydrofluoric acid and nitric acid are used for pickling, which poses a great hazard to the operator as well as the environment.
Modern Safety Improvements
- Use of citric acid based pickling agents reduces risks compared to traditional nitric and hydrochloric acid barriers
- Improved training programs for personnel on safe work practices
- Emphasis on using Personal Protective Equipment (PPE)
- Providing adequate air flow and ventilation systems
- Implementing proper chemical disposal systems
Benefits of Pickled and Passivated Stainless Steel
The processing of pickled and passivated stainless steel (SS) is highly beneficial to the efficiency of the operation and preservation of the SS elements. The most important advantages include:
Enhanced Corrosion Resistance
Protecting stainless steel from environmental corrosion involves creating a Ga-free, protective, chromium rich surface oxide film. The surface of these materials are often treated using pickling or passivation – which eases the cleaning and strengthening of the surface. As learned from recent statistics, as well as the results of Google keyword analysis, one can state that there is more need for materials which do not easily rust in the fields of marine structures, chemicals, as well as the food industry.
Improved Aesthetic Appeal
Aside from functionality, stainless steel offers a clean and contemporary look, thus making it the favoured material by many designers. Due to its shiny surface and ability to retain its luster, the preference for pickled and passivated stainless steel is not only applicable to construction, home or office manufacture, decoration etc. Analysis of the data accessed from the latest indices of the Google search engine reveals another trend: increasing interest in materials with minimum design, which is good looking, for interiors of kitchens, showers, and the like or for constructing modern buildings.
Increased Durability of Steel Pipes
Thanks to material science and manufacturing improvements, durability of steel pipes improved a lot. In new reports generated by the search engine of Google there is recorded a growing attention towards the more corrosion resistant and higher strength alloys of steel. The new designs ensure that steel pipes can be used to extreme environmental conditions or factors high pressures, changes in temperature, moisture or chemicals.
Applications of Pickled and Passivated Stainless Steel
| Industry | Applications | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Food and Beverages | Equipment for foodstuffs processing, storage tanks, piping systems | Ensures health and safety, sanitary standards, no contamination or corrosion |
| Chemical Industries | Chemical tanks, reactor vessels, piping systems for corrosive substances | Film formation ability, inactive nature of material |
| Medical Sector | Surgical instruments, medical furnishings, sterilization ware | Poor microbial growth, withstands hygienic cleaning agents |
| Building and Construction | Architecture, bridge construction, marine infrastructure | Durability, resistance to hostile environmental conditions |
| Pharmaceutical | Reactors, pipework, storage tanks | Food grade and sterile production operations, absence of contamination |
Industry Use Cases for Steel Pipes
Oil & Gas Context
Steel pipes play a pivotal role in all three stages of the oil and natural gas value chain from exploration extraction to transportation. They offer excellent characteristics against high pressure, corrosion extreme temperature – suitable for both onshore and offshore pipelines.
Construction and Infrastructure Sector
Structural or plumbing systems, steel pipes find extensive use in construction industry. Their strength and elasticity permits them to construct high rise towers, bridges, or factories as a matter of fact.
Automotive Context
Steel pipes are critical in the manufacture of exhaust systems and fuel lines, among others. Each one of those parts is ensured together with its related systems by virtue of their capacity to resist mechanical stress.
Energy & Power Generation
Including power plants where steam delivery systems are required at high temperatures and pressure. They also form key elements for motors that are used for windiness generation where towers are constructed of these pipes.
Water Equipment and Sanitation
Steel pipes are largely used in urban water infrastructures for both the supply of fresh water as well as the disposal of waste water because of their durability and ability to minimize leakage.
Production and Processing Industries
Steel pipes find application in machines, aircraft parts, manufacturing enterprises, various industries where piping of chemicals, gases and other substances is required.
References
-
Utah State University: Explains the chemical cleaning process of metals, including degreasing, pickling, and passivating steps, and their effects on metal surfaces. Read the chapter.
-
National Capital Planning Commission (NCPC): Discusses the use of pickling and passivation in corrosion-resistant materials for the Eisenhower Memorial, highlighting its role in removing discoloration and enhancing durability. Access the document.
-
Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory: Provides a detailed handbook on the pickling and cleaning of stainless steel, including procedures for passivation and decontamination. View the handbook.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What do Pickling and Passivation Mean in Steel Processing?
Pickling as a process as well as, Passivation is another complementary process that takes place on the steel surfaces of components in order to enhance their scale resistance. Pickling is the process of removing scale or other oxides layers using a respective acid soution and passivation is the formation of protective passive film on the surface of steel to aid in corrosion resistance.
How Pickling Aids in the Removal of Stains From Stainless Steel Metal?
As the name suggests in pickling, the outermost layer of oxides along with some stains can be scraped off from the surface of the stainless steel. Generally, this practice makes use of the acidic solution in order to remove and clean the surface of the metal so that the passivation film will adhere better.
Why Passivation Can Be Considered a Useful Method for Increased Corrosion Resistance?
The aim of passivation is to form a protective layer on the surface of stainless steel, which is usually a film. The film formed in the process considerably enhances the corrosion resistance of stainless steels, in particular, steels of high nickel austenitic alloys.
Why is Pickling and Passivation Necessary for Stainless Steel Components?
Its significant to pick, and passivate stainless steel components to maintain their corrosion activity and durability. These operations are necessary to eliminate grease and other pollutants that would adversely protect the steel.
What is the ASTM Guideline of Treatment through Passivation?
The ASTM A380 specifies the procedures for cleansing stainless steel parts, and descaling them for cleaning purposes. According to this guideline, the modifications stated increase the level of corrosion resistance of the stainless steel toward the exposure experienced.
How Does Electropolishing in Passivation Function?
Each of these sterile instruments, such as scissors and other simple tools in a standard operating room, is always expected to have been pickled and passivated before sterilization, vó”> or done any similar cleaning process itself.
Is Pickling and Passivation Suitable for Carbon Steel?
While arguably associated more with the stainless steel fabrication process, pickling and passivation can actually be used in the construction of the carbon steel parts as well for the purpose of contaminant removal and surface conditioning. Still, a note of caution should be raised here as the efficiency as well as the level of protection from corrosion may not be the same as in case of therapies associated with stainless steel.
How Does Passivation Aid High Nickel Stainless Steels?
Passivation is a beneficial process, especially for stainless steel with high nickel content, due to the formation of a protective passive layer on the material’s surface. Such a layer gives good resistance to corrosive attack and facilitates manufacture of structures that will resist the aggressive action of the environment.
What Should I Do to Sufficiently Pickle and Passivate My Metal Products?
In order to accomplish pickling and passivation, it is important to ensure that recommended procedures are adhered to, including the appropriate use of acids and proper time and temperature factors. Consulting and keeping up-to-date on the standard techniques of doing so accompanied by the adequate use of materials enhance the stainless steel parts’ corrosion resistance properties.







