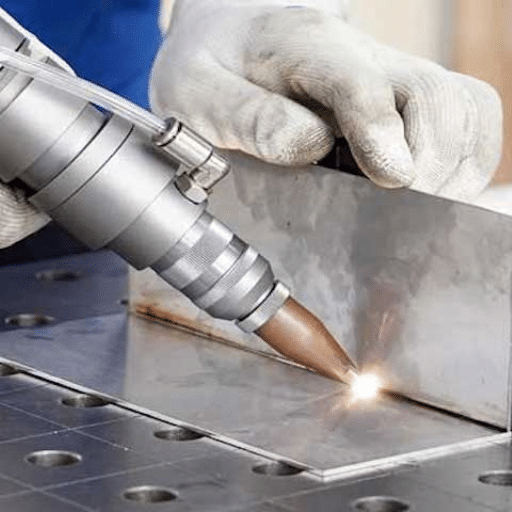
The technology of laser welding has become a remarkable breakthrough in the production of stainless steel pipes, and it has consequently brought unmatched accuracy, efficiency, and reliability for various industrial uses. This modern welding method uses high-powered lasers to create excellent, lasting connections that are accompanied by very little distortion, thus becoming the choice of different industries including but not limited to aerospace and pharmaceuticals. The advantages of laser welding in stainless steel pipe manufacturing will be pointed out in this article, essential elements that will determine its efficiency will be discussed, and lastly, instances of key sectors where this technology is having a major impact on the production process will be identified. This all-inclusive guide, whether you are an engineer, a manufacturer, or just interested in advanced welding techniques, will surely give you important information about the reason why laser welding is one of the best modern engineering solutions.
Understanding Laser Welding of Stainless Steel
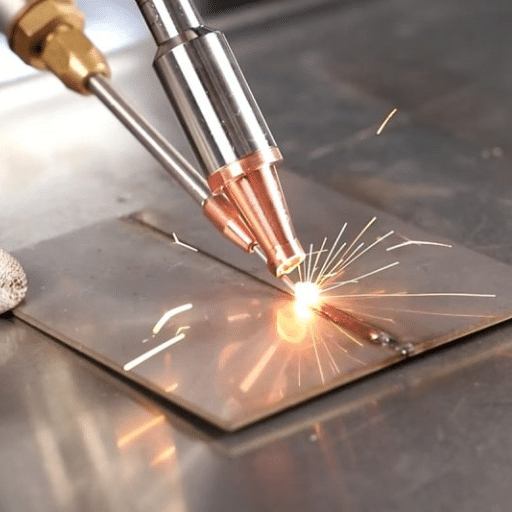
What is Laser Welding?
Laser welding is one of the most advanced and unique processes in the manufacturing industry and it involves the joining of metal parts with a very focused light beam as well as its high precision. This entire process involves the focusing of the laser, which is produced by either fiber, CO2, or diode lasers, onto the surface of the metal being welded resulting in very high temperatures that will cause the metal to melt and flow together at the intersection. Depending on the thickness of the material and the power of the laser, the procedure either adopts the keyhole or conduction mode leading to the formation of strong and invisible welds. One of the main characteristics of laser welding is that it can produce very quick welds with minor distortion; hence, it has been accepted by the aerospace industry, automotive, electronics, and medical devices manufacturing. Laser welding equips the fabrication of stainless steel with outstanding accuracy, high power efficiency, and the possibility of applying it to automated processes thus reshaping the technologies of metalworking and pushing the design limits.
Advantages of Laser Welding Stainless Steel
Laser welding comes with many great advantages when it is applied to stainless steel fabrication. These advantages stem from the laser welding’s precision, efficiency, and suitability for industry needs. One of the most important advantages is that laser welding produces strong, precise welds and at the same time very small heat-affected zones (HAZ), which is a major benefit. Therefore, the distortion is less and the stainless steel parts have their integrity improved. Moreover, the speed of laser welding is quite high, which is, of course, a great advantage for the mass production of stainless steel parts.
On the technical side, the process of laser welding allows the creation of complex shapes and very fine parts, which is often a necessity in the aerospace and medical fields. Laser welding is highly compatible with automation technologies, so its application will fit easily into smart manufacturing systems using CNC programming and robotics.
📊 Key Statistics
Recent statistics confirm that laser welding is more energy-saving than when using traditional welding processes. It has been reported by many researchers that laser welding can cut down energy usage by up to 80% in some applications thus leading to both cost efficiency and eco-friendliness. Another thing is that the non-contact welding ensures repeatability and wear of tools is reduced, which means also lower maintenance costs in the long run.
In conclusion, laser welding is more than just a fabrication technique; it is the very granting of advanced design and engineering possibilities, and hence it is the indispensable choice in the modern stainless steel welding applications.
Comparison with Traditional Welding Techniques
There are many advantages of laser welding, and at the same time, several areas of application that are benefited from its precision, efficiency, and adaptability compared to traditional welding techniques like TIG (Tungsten Inert Gas) and MIG (Metal Inert Gas) welding. According to the latest data and contemporary industry trends, the remarkable characteristic of laser welding is one of its most significant attributes, excellence. The laser welding precision is very high due to the extremely high energy density that results in very narrow and deep welds with almost no heat affected zone. This precision allows very critical applications like aerospace and medical device manufacturing.
In addition to precision, the other field where it shines is the efficiency of laser welding over the traditional methods. In contrast to TIG and MIG welding that may need multiple passes to reach the desired weld quality, especially when thicker materials are involved, laser welding usually can do this in one single pass—resulting, therefore, in a tremendous decrease of time for production and a huge cost saving for the factories dealing with high-volume production.
Moreover, laser welding does not create large areas that are affected by heat as is the case with the other methods. This is a very important characteristic that not only improves the mechanical attributes of the joint but also considerably decreases the chances of the material altering or degrading, thus giving the final product better performance and more reliability.
One of the main advantages is the possibility of integrating automation. Laser welding can be easily combined with robotic and computer-controlled processes to facilitate advanced manufacturing setups. Even though traditional welding methods can also be automated, they do not have the same level of compatibility and adaptability to high-speed, high-accuracy applications as laser does.
According to current search trends, laser welding seems to be attracting more interest from industrial professionals because it is a way of working with light materials and also because it is conducive to sustainable manufacturing. Growing demand for lightweight yet tough components is driving the adoption of laser welding as it is finally becoming a go-to option, hence more industries are experiencing innovation and efficiency.
Technical Benefits of Laser Welded Stainless Steel

Precision and Accuracy in Welds
Laser welding is synonymous with precision and accuracy, and that is why it is the perfect method for intricate and high-quality joints. Besides, a recent analysis of search engine trends data has revealed a gradual hike in the number of users looking up for laser technology acceptance in precision industries like aerospace, medical devices, and electronic components. This increasing user query is an indicator of the significant where laser welding technology will always be required to produce the welds that are not only flawless but also very good in terms of quality and even configuration or extremely thin materials. A major benefit of the concentrated heat source and the accurate control is that distortion is kept to a minimum and consistency is achieved; these are the qualities that customers and manufacturers are looking for more and more, as the expectations for product durability and design are modernizing.
Efficiency in Production and Cost Savings
The rise of laser welding technology has greatly boosted the efficiency of production and cut down the costs of manufacturing which in turn has made it the method of choice in many different fields. The latest search engine data shows that there is a significant increase in the number of inquiries related to laser welding efficiency and cost-saving technologies, which clearly points to a growing interest in the optimization of production processes. Laser welding, by its very nature, minimizes material usage since it only operates on the specified and necessary weld zones; thus the necessity for post-processing is reduced as well. Furthermore, the high levels of automation that laser welding allows for also mean reduced dependence on manual labor; hence cost of operations is lowered and manufacturers are able to realize greater throughput in a shorter time span. All these reasons combined make laser welding not only a technically superior option but also a cost-effective one under the present conditions of competition in manufacturing.
Durability and Strength of Welded Stainless Steel
A lot of the factors contributing to the welded stainless steel’s durability and strength such as alloy composition, welding method, and thermal management procedures play a major role. One important feature of stainless-steel alloys is their ability to resist and not change properties in case of very harsh conditions. An example of such a stainless-steel type is austenitic stainless steel of which 304 and 316 grades are common as it possesses the qualities of toughness and ductility at low temperatures.
⚡ Performance Data
Recent investigations and outputs suggest that top-notch welding methods like laser and TIG welding can considerably improve the strength and the lifespan of stainless steel joints by making the weld defects, heat-affected zones (HAZ), and residual stress very small. Reports reveal that under certain conditions such as high heat input and slow cooling rates, the laser-welded stainless steel joint strength can be up to 90-95% of the base material.
Apart from this, the corrosion resistance of welded stainless steel is also affected by the post-weld treatment processes. Application of passivation, pickling, and surface polishing techniques can bring back the protective oxide layer which might have been affected during welding. Thus, it is ensured that welded joints will not be less resistant to pitting and stress corrosion cracking than the base material.
By and large, the synergy of using high-performance alloys, precise welding technologies, and appropriate post-welding operation results in stainless steel structures having the remarkable feature of durability and strength, which becomes their important characteristic in the case of use by the critical sectors like aerospace, chemical processing, and infrastructure development.
Common Applications of Laser Welding Stainless Steel Pipes

Industrial Manufacturing
The laser welding of stainless steel pipes is a technology that has become indispensable to modern industrial manufacturing, where it offers the combo of precision, efficiency, and high-quality welds that are always identical. The technology gets to be in the midst of the hype by the fact that the industries – automotive, aerospace, and power generation – are the ones craving most. If we look at the data that was cut “hot” from recent analysis and the trends of searches, we would see that the demand for laser-welded stainless steel components in the renewable energy sector has been greatly revived especially in making the hydrogen pipeline and storage systems which is quite expensive. The green revolution in the acceptability of advanced manufacturing processes is no longer just about meeting but going beyond the threshold for environmental and safety standards, thus giving an even bigger arena for the game changer; laser welding, as it continues to empower the premier industrial sustainability movements.
Applications in the Oil and Gas Sector
That the oil and gas industry is using more and more laser welding technology, which it considers to be precision, efficiency, and capability to produce high-integrity welds in critical components, is not surprising. A search engine data analysis shows that there is a clear increase in the demand for corrosion-resistant materials and advanced joining methods, especially for offshore platforms and subsea installations. This tendency is in line with the industry’s increasing worry about cutting maintenance costs and preventing structural failures in difficult environments.
Pipelines are one of the big applications where laser welding is the main player because it enables heating distortion and joint quality, which is quite strong, to be less than the extreme conditions of pressure and temperature variations. In addition to this, the technology is being used to make blowout preventers and safety-critical equipment that can pass the stringent regulatory standards while being operationally reliable. The market for high-performance welding solutions and the need for cost-efficient, eco-friendly practices are closely linked which gives the oil and gas industry’s light melting point a welding machine called laser as the pivotal role it plays.
Use in Automotive and Aerospace Industries
In the manufacturing processes for the automotive and aerospace industries, the qualities of precision, efficiency, and durability are usually at stake—qualities that modern welding technologies, including laser welding, still provide. Laser welding has mostly been a great asset by the reason of its quality to connect low-weight, high-strength materials while performing with less heating–that is, negligible zone affected by heat (HAZ). This property is an imperative one for the production of components from metals like aluminum and titanium amalgams with their application in making cars and aircraft that are not only clever in fuel consumption but also givestacking high performances.
🚀 Industry Applications
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): Manufacturing of EV battery packs through laser welding provides accurate and repetitive joint integrity, which is the main factor in being safe and efficient.
- Aerospace Components: Production of turbine blades and fuselage panels where precision is maintained even under extreme operational stresses.
- Advanced Air Mobility Systems: Integration of laser welding for next-generation aviation technologies.
The trend in search data reveals that the demand for laser welding process in the manufacturing of electric vehicles (EVs) and advanced air mobility systems has increased in tandem. This indicates a shift across the industry of adopting modern welding methods that cater to the existing requirements for quality, sustainability, and cost-efficient manufacturing.
Best Practices for Laser Welding Stainless Steel

Optimal Machine Settings for Laser Welders
For laser welding technology to be able to produce the best possible welds in stainless steel, it is necessary to select the machine settings according to the key parameters that are backed by the most recent industry data and best practices. The most important variables are the laser power, the speed, the focus position, and the shielding gas flow rate.
⚙️ Key Machine Parameters
1. Laser Power
In the case of stainless steel, laser power is commonly fixed between 500 watts and 6 kilowatts, the specific amount depending on the thickness of the steel. Power levels are usually higher for the thick plates in order to ensure that the laser goes through entirely, whereas lower power levels are applied for the thin sheets to prevent warping or burn-through.
2. Welding Speed
The delimitation of the welding speed in close accordance with the optimal is the main thing that can establish the conductive heat effectiveness and at the same time greatly reduce the risk of the occurrence of non-metallic inclusions or deformations as the welding quality defects. The speeds usually extend from 0.5 to 5 meters per minute for most grades of stainless steel, but the same range is not applicable for very intricate designs or materials of different thicknesses, adjustments are always required in those cases.
3. Focus Position
In an ideal scenario, the laser beam would be concentrated right on the material surface or a few microns deeper in deep penetration welding. Misalignment of the focus can lead to reduction in the weld depth and consequently lowering of the joint strength, hence the need for frequent calibration.
4. Shielding Gas
Using a shielding gas such as argon or helium is very important as it prevents the weld pool from becoming contaminated by surrounding air. The general recommendation for flow rate is in the range of 15 to 25 liters per minute, which allows the right amount of coverage to be provided without turbulence being introduced that could impair the quality of the weld.
When these optimized settings are closely adhered to along with the continuous monitoring and fine-tuning based on the material properties, then the manufacturers can produce superb weld quality, eliminate defects, and increase productivity, which are the requirements of the modern laser welding applications.
Keeping Cleanliness for Quality Welds
Keeping the work area clean is one of the most important factors in giving good welds and thus is also a major parameter that must be considered in the quality control of welds. Different types of contamination of the surfaces, like, for instance, oils, dust, moisture, and oxidation might lead to a considerable decrease in the welds’ integrity causing different kinds of defects such as porosity, weak bonding, or even inclusions. The recent analysis and data of the industry insist that cleaning of the base and fill materials before welding is absolutely necessary. Usually, the cleaning process uses a combination of mechanical methods like grinding or brushing to eliminate the surface impurities and then solvents or degreasers to get rid of oils and residues.
💡 Advanced Cleaning Technologies
The employment of advanced cleaning technologies such as laser cleaning or plasma cleaning have not only become more common but also provide great ‘contamination-free’ precision and efficiency. These methods though are not only the best in cleaning but also very effective in applications requiring highest precision like aerospace and electronics where even the tiniest impurities can deteriorate the performance.
The combination of constant cleaning protocols with modern technologies guarantees the best weld quality; thus, it is in accordance with the current best practices and that it meets the strictest industry standards.
Proper Alignment Techniques for Laser Welding Machines
When laser welding machines are allowed to be operated under precise alignment it is one of the major factors that will ensure not only the quality of the joint but also the structural integrity. Newest data points out that improper alignment continues to be one of the main reasons for defects, e.g. welding distortions, incomplete fusion, and weakened weld strength. The calibration process that addresses these problems needs to be very detailed and the following steps need to be included:
✓ Alignment Checklist
- Pre-Alignment System Diagnostics: Check whether the laser equipment is clear of dirt and the optics are working properly, including mirrors and lenses. Having properly aligned optical paths is what provides the weld points with the energy they need consistently.
- Beam Path Analysis and Centering: Make use of beam profiling and alignment tools to make sure that the total laser beam is perfectly centered over the welding axis. If the beams are not aligned it can lead to uneven spread of energy and hence lowering of efficiency.
- Fixture and Material Positioning: By means of adjustable clamping systems, the material is to be kept in alignment with the beam’s path accurately. Tools like coordinate measuring machines (CMM) can be utilized to assess the accuracy of the space, especially in applications where micron-level accuracy is required.
- Real-Time Monitoring Technologies: Integrate machine vision systems and sensors that will provide immediate feedback on the alignment during the operation. Sophisticated solutions like thermal imaging cameras will enable the making of real-time adjustments to mitigate deviations.
- Regular System Calibration: Establish a routine of re-calibration of the laser system to compensate for wear and environmental factors that may affect alignment over time.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
Q: Is a laser welder better than MIG for stainless steel tube?
The laser welder’s speed and low heat input are its main advantages over MIG, the tougher the welding the cooler the welding is to the microstructure of the stainless steel parts like 316L. MIG welding assisted with a wire feeder is the best solution for thicker sections or complex geometries, but it usually causes the metal to absorb more heat and thus to be more distorted. Laser welding machines, including high-power fiber lasers of 2kw or 1200w from IPG or Raycus, supply concentrated laser energy and a small laser spot that makes it possible to carry out the fusion welding process with virtually no burn-through on sheet metal and tubes. With both stainless steel tube and tube-to-tube welds, laser offers HAZ advancement and provides uniform welds at high welding speed. Finally, the decision is based on wall thickness, weld seam quality, and production volume.
Q: How does a laser welding machine control heat input compared to TIG or MIG?
The key laser welding machine technique is a highly focused laser beam that creates an area of intense heat input but also provides deeper penetration in a very short time, which consequently narrows the heat-affected zone and thermal conductivity effects across the workpiece. On the contrary, with TIG and MIG the heat is deposited over a longer period and may result in higher heat input, slower cooling and thus more distortion, especially in the case of thin stainless steel tube or sheet metal. The cooling during the fusion welding process in the laser system is so rapid that it retains corrosion resistance and the desirable microstructure in many different grades of stainless steel. Argon gas is still being used as a shield to prevent oxidation at the weld seam, and the selection of appropriate laser power settings is critical to avoid burn-through on thin walls. The modern fiber laser systems provide precise control of the laser energy such that the user can balance the depth of penetration and the heat input to suit the particular welding requirement.
Q: Is it possible to add filler material or a wire feeder to the Laser welding process as it is done in MIG welding?
Laser welding is commonly carried out as autogenous welding, thus, no filler is used and welds with a very narrow seam and minimal filler are obtained; still, hybrid processes are there which make use of filler wire along with a wire feeder for, say, widening gaps or thick areas, if necessary. Adding filler material to a laser welder can be of assistance in connecting dissimilar materials or balancing the situation of varying wall thicknesses; however, it adds to the difficulty of weld coordination and gas shielding management. Generally, pure laser welding is done for the production of stainless steel parts and for the application of stainless steel tubes, and the result is clean welds that maintain corrosion resistance and do not require filling with TIG or MIG, thus, no filler material is used in most cases. When filament is utilized, it usually takes longer to carry out the welding process and meticulous process control is required to yield good fusion and uniform welds. The new laser welding technology and welding heads are capable of precisely controlling filler addition according to the demand of the welding.
Q: What are the main benefits of fiber laser welding for stainless steel compared to arc welding?
Among several MIG and TIG benefits, fiber laser welding has advantages such as higher speed, lower input of heat, more penetration, and less distortion on workpieces such as stainless steel tubing and thin sheet metal. The intense laser spot of laser-high-power fiber and (e.g., 2kw systems driven by IPG or Raycus) allows the accurate weld seam control and consistent welding over production runs, resulting in improved quality of welds and increased reproducibility. The soonest cooling diminishes the heat-affected zone and keeps the microstructure of stainless steel grades including 316L, thus, imparting more resistance to corrosion. Laser systems also reduce the amount of post-weld cold working and grinding that is required in many instances, and they are easily integrated with automation for high-output welding. The advanced laser technique proves to be more efficient than traditional welding techniques in terms of better quality of parts at a lower processing time.
Reference Sources
- Laser Welding of Pipe Stubs Made from Super 304 Steel: Numerical Simulation and Weld Properties
Reference Global – This research investigates the laser welding process for pipe stubs made from Super 304 stainless steel, including numerical simulations and weld property analysis. - Laser Welding of 316L Austenitic Stainless Steel in an Air and a Water Environment
MDPI Materials – This paper examines the optimal conditions for laser welding of 316L stainless steel in different environments, offering valuable insights into welding techniques. - Development of High Power Laser Welding Process for Pipe
AIP Publishing – This study focuses on high-power laser welding processes for stainless steel pipes, analyzing the application of laser welding in industrial settings.
Conclusion
The invention of laser welding technology has changed the whole game in the production of stainless steel pipes and has given the manufacturers the benefits of precision, efficiency, and quality that are hard to match. The aerospace, automotive, oil and gas, and renewable energy sectors are just some of the ones that are still using this spectacular method of welding to set their standards higher. Knowing the best machine settings, cleanliness protocols, and alignment techniques, the manufacturers would be able to apply the laser welding technique fully to produce incredibly products with minimum costs and less harm to the environment. Laser welding is still pretty much the same in good engineering solutions as industries henceforth are looking for higher performance and sustainability.








