📊 Approximately 500 steel mills operate across the United States
🏭 Around 100 active integrated mills currently in operation
📈 Annual production capacity: ~80 million metric tons
Current State of the Steel Industry

The U.S. steel industry currently operates with approximately 500 steel mills nationwide, ranging from large-scale integrated operations to smaller mini-mills. These facilities are categorized into two primary types:
- Integrated Mills: Use raw materials such as iron ore and coal to produce steel from scratch
- Mini-Mills: Primarily use recycled steel scrap as their main input material
Total Number of Steel Mills in the US
According to recent industry estimates, the United States hosts approximately 500 steel manufacturing facilities. This number encompasses:
- Large-scale integrated steel plants
- Electric arc furnace (EAF) mini-mills
- Specialty steel producers
- Regional and local steel manufacturing operations
The majority of current production comes from mini-mills, which have gained prominence due to their efficiency and sustainability advantages in steel recycling.
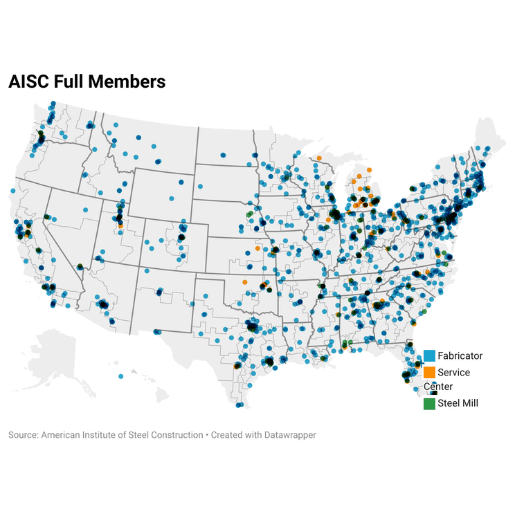
Geographic Distribution of Steel Plants
Steel mills are strategically distributed across the United States, with notable concentrations in specific regions:
| Region | Key States | Characteristics |
|---|---|---|
| Great Lakes | Pennsylvania, Ohio, Indiana | Traditional steel belt with integrated mills |
| Industrial Northeast | New York, New Jersey | Historic steel centers with modern facilities |
| South | Alabama, Texas | Rapid expansion of mini-mills |
| Midwest | Illinois, Michigan | Mix of integrated and mini-mill operations |
Major Steel Cities
- Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania – Historical steel capital
- Gary, Indiana – Major integrated steel production
- Birmingham, Alabama – Southern steel hub
- Houston, Texas – Growing mini-mill presence
Types of Steel Produced in American Mills
American steel mills manufacture various types of steel to serve different industries:
Primary Steel Types
- Carbon Steel: Cost-effective option for construction and civil engineering
- Alloy Steel: Enhanced strength with added elements like chromium, nickel, or vanadium
- Stainless Steel: Corrosion-resistant steel for household and medical applications
- High-Strength Low-Alloy (HSLA) Steel: Lightweight, high-strength steel for automotive and aviation
- Tool Steel: High-temperature resistant steel for cutting and machining applications
Economic Importance of the Steel Manufacturing Sector

The U.S. steel industry directly employs approximately 1.2 million people and supports millions more jobs in related industries.
Key Economic Contributions
- Direct and indirect job creation across multiple sectors
- Support for construction, automotive, and manufacturing industries
- Significant contribution to international trade and export revenues
- Technology advancement and innovation driver
- Infrastructure development enabler
Impact on Related Industries
The steel industry serves as a cornerstone for numerous sectors:
| Industry | Steel Usage | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Construction | Structural steel, rebar | Essential for infrastructure and building projects |
| Automotive | Body panels, frames | Critical for vehicle manufacturing and safety |
| Renewable Energy | Wind towers, solar mounts | Enables green energy infrastructure |
| Manufacturing | Machinery, tools | Foundation for industrial production |
Trends and Innovations in Steel Manufacturing
Environmental Sustainability
- Electric Arc Furnaces (EAF): Reduced carbon emissions through scrap steel recycling
- Hydrogen-based Direct Reduction: Alternative to coal-based production methods
- Carbon Capture Technologies: Advanced systems to reduce CO2 emissions
- Renewable Energy Integration: Green electricity sources for steel production
Technological Advancements
- Industry 4.0 integration with AI and IoT systems
- Advanced automation and robotics
- Digital monitoring and predictive maintenance
- 3D printing and powder metallurgy applications
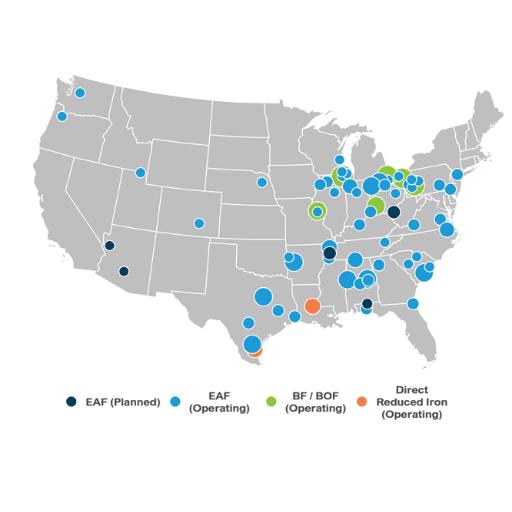
Challenges Facing the American Steel Industry
Economic and Competitive Pressures
- Competition from low-cost international producers (China, India)
- Trade policy uncertainties and tariff fluctuations
- Price volatility in raw materials and energy costs
- Supply chain disruptions and logistics challenges
Environmental and Regulatory Challenges
- Stricter environmental regulations and compliance costs
- Carbon footprint reduction requirements
- Investment needs for cleaner technologies
- Balancing environmental goals with economic competitiveness
Workforce and Skills Gap
- Aging workforce and knowledge transfer challenges
- Need for skilled workers in modern steel technologies
- STEM education and vocational training requirements
- Recruitment and retention in competitive job markets
Market Trends and Future Projections for 2024
Growth Drivers
- Infrastructure development and urbanization projects
- Electric vehicle manufacturing expansion
- Renewable energy sector growth
- Advanced manufacturing and technology applications
Sustainability Focus
- Increased investment in green steel technologies
- Hydrogen-based production methods
- Enhanced recycling and circular economy practices
- Carbon-neutral steel production goals
Global steel consumption is expected to continue growing, driven by emerging market infrastructure development and increased manufacturing capacity.
A Brief History of Steel Manufacturing in the US
Key Historical Milestones
| Period | Development | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Late 1800s | Bessemer process introduction | Cheaper, more efficient steel production |
| Early 1900s | U.S. Steel Corporation formation | Industry consolidation and expansion |
| World War II | Massive production increase | U.S. became global steel leader |
| 1980s | Industry restructuring | Plant closures and modernization |
| 2000s-Present | Technology and sustainability focus | Green steel and efficiency improvements |
Modern Era Achievements
- Current annual production: approximately 80 million metric tons
- Over 70% of production now uses electric arc furnaces
- Significant reduction in energy consumption and emissions
- Focus on high-quality, specialty steel products
References
-
Appendix C: EAF Steel Facilities – National Academies Press – Provides detailed information on Electric Arc Furnace (EAF) steel facilities in the U.S.
-
U.S. and Global Iron and Steel Industries – University of Alabama – Discusses the primary steel-manufacturing states and industry trends.
-
Domestic Steel Manufacturing: Overview and Prospects – Congress.gov – Offers insights into the distribution of mini-mills and integrated mills across the U.S.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
How many steel mills are in the US?
The United States has around five hundred steel production establishments that meet the definition of a steel mill, though these plants vary widely in both their size and nature leading to different proportions of crude steel produced in the country as a whole.
What Type of Steel Does The American Steel Mills Make?
Various types of steels are produced in the US steel mills. These can be classified as carbon type of steel, alloy type of steel and other specialized types of steels. The production of steel in mini-mills, and also the integrated steel mills, in part relies on recyclable material which nevertheless does not inhibit the meeting of industry constraints on the qualities of products considered.
What are the Functions of the Integrated Steel Mills in the United States?
The integrated steel mills in the United States have a pivotal role in making steel from the basic ingredients like iron ore and other raw materials. They perform such functions as manufacturing molten iron using the basic oxygen furnace, which is then converted to crude steel and rolled into different sections of pipes and tubes.
What is the Steel Production Output in the United States?
The steel production capacity of the United States is outstanding at about 79 million metric tons per annum, which ranks the country among the world’s top steel-producing nations. The importance of this output cannot be understated as it provides the necessary support for domestic manufacturing as well as infrastructural growth.
Which States Have the Largest Steel Production Units and How Many Steel Mills Are in the Us?
Most of the largest steel plants in the Us are found in such states as Indiana and Pennsylvania, which have been major centers for the steel industry since the turn of the 19th century. Today, these areas boast of numerous heavy manufacturing plants that focus on producing steel that is made efficiently in smaller units referred to as minimills.
How does Technology impact Steel Production?
In this day and age, marked by remarkable development in technology for steel, a number of approaches have been adopted to improve efficiency in some areas of steel production: reducing man power per ton of finished steel and reducing carbon emissions. Such innovations improve the quality of the final product as well as permitting the solution of some ecological problems.
What about U.S. Steel Mills – is Their Output Comparable With Others in the World?
The usa steel industry is amongst the largest steel makers and in the meanwhile the largest steel consumer. While in the countries like China steel production reached 600 million tons plus and still counting every year, the USA steel industry has engaged in quality and innovation in steel making.
Then How Does the Prospects of the American Steele Industry Looks Like?
Prognoses are favorable also in the USA, as there are works in progress directed towards improvement of the existing steel manufacturing processes and incorporating ‘green’ methods into production. It is forecasted that as long as the present steel consumer goods will be required in growing quantities, the steel manufacturing in the country will also adjust and transform so as to enhance the present capabilities vis-a-vis the production of high-quality steel.







