Key Takeaway: Valve systems play essential roles in many sectors, controlling the movement and flow of liquids, gases, and slurries within a particular system. Selecting the wrong valve can affect the efficiency, operation, and safety of industrial processes.
Introduction to Industrial Valves
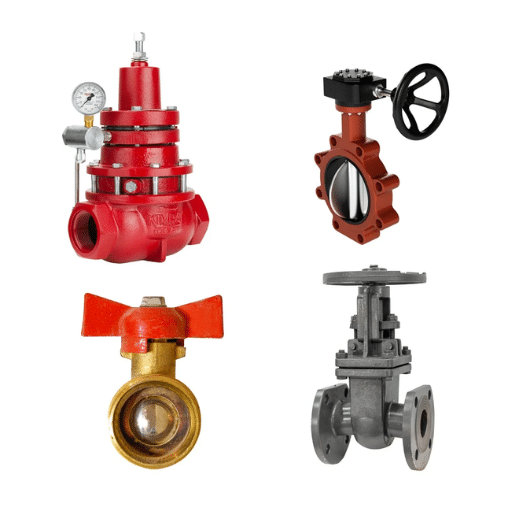
Industrial valves manage the movement of fluids or gases within closed systems and are crucial components across multiple industries including oil and gas, water purification, chemical production, and manufacturing. These mechanical devices regulate, steer, and contain matter by opening, shutting, or creating partial obstacles in pipes.
What is an Industrial Valve?
An industrial valve is a mechanical system designed for regulating, steering, and containing gases, liquids, and slurries as they move from one point to another within a given system. Modern valves incorporate advanced features capable of sustaining high pressure and temperature levels while resisting corrosive solutions for extended periods.
Importance of Valves in Industrial Applications
| Function | Description | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Flow Control | Regulate liquid and gas transport in industrial processes | Maintains optimal pressure drop and uninterrupted flow |
| Safety Mechanisms | Protect equipment and prevent process discontinuation | Critical for high-pressure and chemical applications |
| Pressure Control | Maintain ideal pressure levels in systems | Prevents overpressure damage and equipment failure |
| Process Efficiency | Optimize system performance and reduce downtime | Increases productivity and operational effectiveness |
| Corrosion Prevention | Use of exotic materials for harsh environments | Extended service life in challenging conditions |
Common Types of Industrial Valves

Gate Valves
Design: Uses a gate mechanism that moves up and down to control flow
Best For: Full bore flow applications requiring on/off operation
Applications: Water purification plants, oil and gas pipelines, power stations
Advantages: Minimal flow restriction when fully open, handles high pressure
Globe Valves
Design: Features a moving disc that closes against a stationary ring seat
Best For: Flow regulation and throttling applications
Applications: Chemical processing, power generation, pharmaceutical industries
Advantages: Excellent flow control capabilities, suitable for high-pressure systems
Ball Valves
Design: Utilizes a hollow, perforated ball to control flow
Best For: Quick shut-off and on/off operations
Applications: Gas distribution, wastewater treatment, HVAC systems
Advantages: Superior shut-off capabilities, durable construction, easy operation
Butterfly Valves
Design: Features a rotating disc for flow control
Best For: Large diameter pipes requiring quick operation
Applications: HVAC systems, water supply, food processing
Advantages: Lightweight, cost-effective, space-efficient
Check Valves
Design: Allows flow in one direction only, preventing backflow
Best For: Pump protection and unidirectional flow systems
Applications: Water systems, fuel systems, chemical plants
Advantages: Automatic operation, prevents equipment damage from backflow
Specialized Valve Types

Check Valve Variations
| Type | Description | Best Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Swing Check Valve | Disc swings open with forward flow, closes against reverse flow | Low pressure, large volume applications |
| Lift Check Valve | Disc lifts when sufficient pressure is applied | High pressure applications with clean conditions |
| Ball Check Valve | Spring-loaded ball permits or stops fluid flow | Handling solids or high viscosity media |
Additional Valve Types
- Plug Valves: Use cylindrical or tapered plugs for flow control, ideal for frequent on/off operations
- Diaphragm Valves: Employ flexible diaphragms for contamination-free applications in food and pharmaceutical industries
- Pressure Relief Valves: Prevent system overpressure in power, chemical, and transport sectors
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Valve
Key Selection Criteria
- Application Requirements: Determine if you need on-off control, flow regulation, or flow diversion
- Operating Conditions: Consider system pressure, temperature, and environmental factors
- Fluid Characteristics: Analyze the type of media (water, gas, oil, chemicals) and its properties
- Size and Flow Rate: Ensure proper valve sizing for required flow without excessive pressure loss
- Material Selection: Choose materials suitable for application conditions and fluid compatibility
- Actuation Method: Select manual, electric, pneumatic, or hydraulic operation based on system needs
- Maintenance Considerations: Factor in lifecycle costs, maintenance requirements, and valve durability
- Standards Compliance: Ensure adherence to industry standards (ANSI, API, ISO)
Industry Applications

| Industry | Common Valve Types | Primary Functions |
|---|---|---|
| Oil & Gas | Ball valves, Gate valves | High-pressure flow control in pipelines and refineries |
| Water Treatment | Butterfly valves, Check valves | Flow regulation and backflow prevention |
| Power Generation | Globe valves, Pressure relief valves | Steam pressure control and equipment protection |
| Chemical Processing | Diaphragm valves, Plug valves | Corrosion resistance and contamination prevention |
| Food & Beverage | Sanitary valves, Stainless steel ball valves | Hygiene maintenance and regulatory compliance |
Advanced Valve Technology and Future Trends
Smart Valves and Automation
Modern valve technology incorporates advanced features including:
- IoT Integration: Sensors and wireless connectivity for real-time monitoring
- Predictive Maintenance: Data analytics to prevent equipment failures
- Remote Control: Central monitoring and operation capabilities
- Energy Efficiency: Reduced power consumption in large-scale installations
- Advanced Materials: Corrosion-resistant alloys and composite components
Market Outlook
The industrial valves market is anticipated to experience exponential growth driven by expanding sectors such as material handling, water distribution, and oil & gas. Environmental regulations and sustainability goals are pushing manufacturers toward eco-friendly valve solutions with reduced CO2 emissions.
References
-
Valves – University of Oklahoma
A detailed PDF from the University of Oklahoma discussing various types of valves, including check valves and their applications.
Visit the site -
Valves – Visual Encyclopedia of Chemical Engineering
A resource from the University of Michigan’s Visual Encyclopedia, providing insights into different valve types like globe valves and their uses.
Visit the site -
Industrial Valves – Academia.edu
A presentation on Academia.edu covering key elements of industrial valves, including ball valves, gate valves, and their advantages.
Visit the site
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What are the categories of industrial valves?
There exist many categories of valves. Some of these categories include ball valves, gate valves, globe valves, butterfly valves, and check valves. These categories of valves are used in diverse ways. They help in the control of flow of liquids in various uses. It is important to know the basic features and uses of these common valve types so as to choose the appropriate one.
When and how does a valve work?
A valve can be described as a system that regulates the movement of water or any other fluid within a piping system. The opening or closing of the valve is done using a handle that is rotated, causing the movement of the internal parts like the stem in order to permit the flow or the closing of the valve. There are different types of valves to operate and each uses a different mechanism which are known as quarter turn and linear motion.
What are the uses of butterfly valve?
Many plant processes involve the use of butterfly valves since these types of industrial valves can be opened and closed very fast. The simple construction enables the use of the valves for fluids and gases relatively easily since the valves are constructions of thin plates. Water treatment plants, air-conditioning systems, and various plant processes will find these types of valves more often.
In what ways can one open a flow control valve without benefit of another pipe?
Different types of Check valves include swing, lift, and ball check. These types of valves have one direction of flow and the possibility of backflow is unacceptable in the system. This determines which type of Check Valve is installed.
What is the use of needle valves in the industrial sector?
Wantle Values are employed where precise flow adjustments require needle valve, turret, or some because of flow characteristics getting into valve partial storage. The key control is in precision of the adjustment is also demonstrated with the help of a long sharp edge stem that the kinematic motion can be confined within fine limits of a task. Such utilization takes place in all systems that contain fluid actuators and pressure, i.e. various hydraulic system control, gas regulation, and other industries that require precise measurement.
Why are valve bodies significant in the operation of a valve?
The valve body is a crucial part of the interdisciplinary contributor as its major function is to contain and mail the outside functioning of the valve. The component is extremely important for the proper functioning of the valve because the high temperature and high pressure from the fluid that is transiting through the valve must be sustained. Valve bodies can be made out of different kinds of materials which will depend more on the application and environment where the valve is to be used.
What is the advantage of utilizing actuated controlled valves other types of industrial valves?
Control valves with actuators provide the benefit of automation of fluid processes thereby increasing their efficiency and dependability. Such valves are remote driven valves and are often employed due to practicality in dealing with large-scale production systems using manual valves. They regulate the flow rates accurately and have the option of incorporating feedback mechanism into the system to control the process in a better way.
What guide do you depend on for selecting a particular valve for an application?
Selecting a valve depends primarily on the understanding of the specific application in question, that is, the nature of the medium, operating pressure, working temperature and required flow rate. Choose the correct type of valve, the right material, and the right operation mode. Furthermore, making appropriate consultation with a valve manufacturer or expert can assist in selecting the appropriate valve for the specified application.







