Manufacturing of seamless pipes has been revolutionizing the steel industry, producing pipes for various applications that are not only strong but also high-performance. Seamless pipes are made without any joints or seams, making them exceptionally strong, reliable, and suitable for the most demanding environments like high-pressure systems, automotive parts, and industrial machines. This comprehensive guide explores the intricate procedure of creating seamless pipes, from selecting raw materials through heating and rolling to achieve the final product shape.
Overview of Seamless Pipe
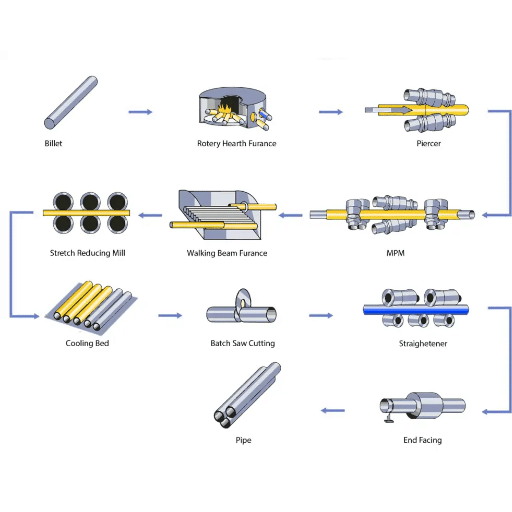
Seamless pipes are cylindrical tubes that are made without a welded seam, thus they are exceptionally durable and reliable under high-pressure and hot conditions. The pipes are made using a solid steel or other materials’ billet that is heated and pierced to create a hollow tube. The removal of seams means no weak points, thus guaranteeing the pipe’s structural integrity and uniform strength throughout.
Key Advantage: Seamless pipes find their use in the oil and gas, power generation, and manufacturing industries quite often. Their precision and performance capabilities make them the preferred choice for applications in harsh environments.
Definition and Benefits of Seamless Pipe
Seamless pipes are extremely strong and reliable cylindrical hollow tubes that are produced without seams or joints. One of the most common ways of making them is by extrusion, in which a solid billet is heated and pushed through a die to produce a continuous hollow tube. This method eliminates the weak spots that are typically found in welded pipes.
Key Benefits of Seamless Pipes:
- Outstanding Load-Bearing Strength: Superior structural integrity without weak points
- Uniform Thickness: Consistent wall thickness throughout the pipe length
- Extreme Condition Resistance: Ability to withstand harsh environmental conditions
- Enhanced Corrosion Resistance: Better resistance to thermal stress and mechanical wear
- Pressure Resistance: Excellent performance in high-pressure applications
- Long Service Life: Durability in demanding operational environments
Applications of Seamless Pipe in Various Industries
Oil and Gas Industry
Superior strength and ability to resist high temperatures and pressure make seamless pipes essential for drilling operations and pipeline systems. Used extensively in exploration, extraction, and transportation.
Growth: Critical for offshore and onshore operations under extreme conditions.
Power Generation
Transports high-pressure steam and fluids in thermal, nuclear, and renewable energy power plants. Ability to withstand fluctuating thermal stresses ensures operational stability.
Application: Essential for nuclear reactor coolant transport under extreme pressure.
Automotive Manufacturing
Used in drive shafts, hydraulic systems, and exhaust pipes. Uniform thickness and precision reduce defects and enhance vehicle performance and safety.
Innovation: Increasingly used for advanced battery cooling systems in electric vehicles.
Construction & Infrastructure
Provides structural support in buildings, bridges, and industrial frameworks. Strongest yet lightweight material for applications requiring environmental stress resistance.
Use Case: Critical for withstanding wind and earthquake stresses in urban construction.
Chemical & Fertilizer Industry
Safe and efficient movement of corrosive chemicals, gases, and fluids. High resistance against chemical degradation from stainless steel and alloyed construction.
Market Growth: Projected CAGR of 5.6% annually due to increased industrial output.
Aerospace Applications
Lightweight components that withstand corrosion in engine systems. Meets tough safety and performance standards for high-altitude extreme conditions.
Advantage: Critical for fuel efficiency and environmental goals in aeronautics.
Comparison with Welded Pipes
The manufacturing processes, mechanical properties, and applications are the main areas where seamless pipes and welded pipes differ the most. Understanding these differences is crucial for selecting the right pipe type for your application.
| Aspect | Seamless Pipes | Welded Pipes |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing Process | Extrusion process – no welded seams | Rolling flat steel plate and welding the seam |
| Structural Integrity | No weak points – uniform strength throughout | Welded joint is a potential weak point |
| Pressure Resistance | Excellent – suitable for high-pressure applications | Good, but limited by weld seam strength |
| Corrosion Resistance | Superior – no seam to corrode | Weld seam vulnerable in corrosive conditions |
| Cost | Higher initial cost | More economical and faster to produce |
| Production Speed | More complex, time-intensive process | Faster production for large volumes |
| Best Applications | Harsh environments, high-stress applications | Less intensive operating environments |
| Reliability | Maximum reliability in critical applications | Reliable for standard applications |
Industry Trend: Data trends report that interest in seamless pipes is growing, mainly owing to their reliability in high-stress applications. Seamless pipes dominate applications where safety and durability are top priorities.
Pipe Manufacturing Processes
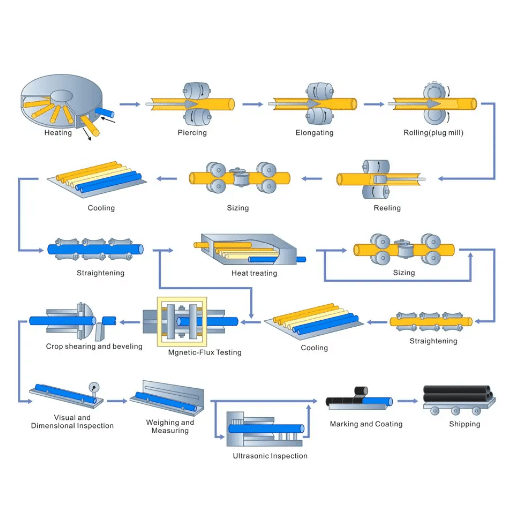
The pipe manufacturing process can be divided basically into two methods: seamless and welded. Understanding these processes is essential for appreciating the unique characteristics of seamless pipes.
Seamless Pipe Manufacturing Overview
Seamless pipes are made by first heating a solid metal block to above its recrystallization point and then drilling a hole through the center of the block to produce a hollow cylinder. The complete process guarantees the homogeneous structure of the pipe, making seamless pipes perfect for applications requiring extreme high pressure, temperature, or structural integrity.
Step 1: Material Selection and Preparation
Selection of appropriate steel grade (carbon steel, alloy steel, stainless steel) based on application requirements. Solid round billets are prepared and inspected for quality.
Step 2: Heating
Billets are heated to temperatures over their recrystallization point, typically 1200-1300°C, in specialized furnaces to achieve optimal malleability.
Step 3: Piercing
The heated billet is pierced using methods such as the Mannesmann process with rotary piercing mills to create a hollow tube shell.
Step 4: Elongation and Rolling
The hollow cylinder is elongated and sized using various rolling processes (plug mill or mandrel mill) to achieve desired wall thickness and diameter.
Step 5: Sizing and Finishing
Final dimensions are achieved through additional rolling or drawing processes, followed by heat treatment and surface finishing.
Step 6: Quality Control
Comprehensive testing including non-destructive testing (NDT), dimensional verification, and stress testing to ensure compliance with standards.
Hot Working Process in Seamless Pipe Manufacturing
Hot working is one of the most critical processes in seamless pipe manufacturing, involving exceptional improvements in the mechanical properties of the material and dimensional accuracy of the pipe.
Hot Working Process Characteristics:
- Temperature Range: Heating to 1200-1300°C, above recrystallization point
- Piercing Method: Mannesmann process using rotary piercing mills
- Rolling Processes: Plug mill or mandrel mill for wall thickness control
- Grain Structure: Controlled deformation produces uniform grain structure
- Material Properties: Enhanced ductility, durability, and stress resistance
- Quality Standards: Strict adherence to dimensional and mechanical specifications
Industry Focus: Recent trends show increasing queries about the hot working process’s efficiency and environmental impact, reflecting the industry’s commitment to sustainability and cost-cutting while maintaining stringent quality and safety standards.
Cold Working Techniques for Seamless Tubing
Cold working techniques are applied methods of processing metal at temperatures below its recrystallization point, thereby improving its mechanical properties, tensile strength, surface finish, and dimensional accuracy.
| Technique | Process | Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Cold Drawing | Tube is pulled through a die to decrease diameter | Enhanced dimensional accuracy and surface finish |
| Pilgering | Series of mandrels and dies successively compress and stretch | Large dimensional tolerances achieved |
| Cold Rolling | Controlled deformation through rolling mills | Enhanced surface finish and uniformity |
Advantages of Cold Working:
- Improved grain structure of the material
- Tighter dimensional tolerances
- Better strength-to-weight ratios
- Perfect material consistency
- Enhanced surface quality
- Minimal material waste with AI-based monitoring
Industry Applications: Cold working is essential in aerospace, automotive, and medical device industries where ultimate precision and material consistency are required.
Quality Control Measures in Pipe Manufacturing
The process of quality control in the pipe production industry is very detailed and primarily aims to guarantee structural integrity, accurate dimensions, and compliance with industry standards.
Non-Destructive Testing (NDT)
| Testing Method | Purpose | Detection Capability |
|---|---|---|
| Ultrasonic Testing | Identify internal defects | Cracks, voids, inclusions without product damage |
| Radiographic Inspection | Detect inconsistencies | Internal structural anomalies |
| Eddy Current Testing | Surface and near-surface defects | Cracks, corrosion, material thickness |
| Magnetic Particle Testing | Surface discontinuities | Surface cracks and defects |
Dimensional Assessment
- Laser Measurement Systems: Precise diameter and wall thickness measurement
- Concentricity Testing: Ensures uniform wall thickness throughout
- Length Verification: Confirms specifications are met
- Straightness Testing: Ensures pipes meet straightness tolerances
Stress Testing
Hydrostatic Testing
Finished pipes are subjected to hydrostatic pressure testing to measure their ability to resist pressure in operation. This ensures the pipe can withstand specified operating pressures without failure.
Advanced Quality Control Technologies
Modern Innovations:
- AI and Machine Learning: Real-time defect detection and predictive maintenance analytics
- Material Traceability: Complete tracking from raw material to finished product
- Performance Analytics: Data-driven process optimization
- Automated Inspection: Consistent, reliable quality verification
- Digital Twins: Virtual modeling for process optimization
Materials Used in Seamless Pipe Production

Seamless pipe production is based on choosing materials with the best mechanical properties and chemical composition to meet rigorous industrial demands. The selection of appropriate material is paramount as it decides the pipe’s lifetime, safety, and compliance with industry standards like ASTM, API, and ASME.
Types of Steel Used for Seamless Pipes
Carbon Steel
Grades: ASTM A106, ASTM A53
Characteristics: Strong, durable, and inexpensive material mainly used for high-temperature service and structural applications.
Applications: General engineering, construction, structural components
Note: May need coating or galvanization for enhanced corrosion resistance
Alloy Steel
Grades: ASTM A335 (P11, P22, P91)
Characteristics: Enhanced with chromium, molybdenum, and nickel for higher performance under extreme conditions.
Applications: Power generation, petrochemical industries
Benefits: Improved strength, toughness, heat and corrosion resistance
Stainless Steel
Grades: 304, 316, 321
Characteristics: Top-notch corrosion resistance for harsh chemical environments.
Applications: Food processing, pharmaceutical, chemical industries
Benefits: Long service life, oxidation protection (higher cost than carbon/alloy)
Duplex & Super Duplex Steel
Grades: UNS S31803, UNS S32750
Characteristics: Combines austenitic and ferritic stainless steel advantages.
Applications: Offshore and marine applications
Benefits: Remarkable resistance to stress corrosion cracking, pitting, and crevice corrosion
Low-Temperature Steel
Grades: ASTM A333
Characteristics: Specially made for low-temperature service, maintains structural integrity in cryogenic conditions.
Applications: LNG facilities, refrigeration systems
Benefits: Excellent toughness at sub-zero temperatures
Nickel-Based Alloys
Examples: Inconel, Hastelloy
Characteristics: Extraordinary ability to withstand high temperatures and chemical corrosion.
Applications: Aerospace, nuclear applications
Benefits: Performance in most difficult conditions
Importance of Material Selection in Pipe Manufacturing
Choosing the right material is one of the most important decisions in pipe making. It has a direct bearing on the product’s life span, safety, and efficiency. According to the latest data and studies from industry sources, poor choice of material can cause failures, costly maintenance, and unsafe operating conditions.
Examples:
- Corrosive Environments: Require 316 stainless steel or duplex alloy to avoid cracking or pitting
- Cryogenic Applications: Low-temperature-grade steels like ASTM A333 maintain toughness at sub-zero temperatures
- High-Pressure Systems: Alloy steels with enhanced strength characteristics
- Chemical Processing: Stainless steel grades for acid and alkali resistance
Alloys and Their Impact on Seamless Pipe Performance
Alloys are one of the main factors that greatly impact the performance of seamless pipes, especially in their most demanding applications. The use of modern alloys significantly enhances pipe capabilities:
| Alloy Type | Key Elements | Performance Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Chromium-Molybdenum (Cr-Mo) | Chromium, Molybdenum | High-temperature strength, corrosion resistance |
| Nickel-Based Superalloys | Nickel, Chromium, others | Exceptional high-temperature performance, oxidation resistance |
| Stainless Steel Alloys | Chromium, Nickel, Molybdenum | Superior corrosion resistance, mechanical properties |
| Duplex Alloys | Balanced austenitic/ferritic | High strength, excellent corrosion resistance |
Alloy Composition Impact:
- Tensile Strength: Significantly increased load-bearing capacity
- Fatigue Resistance: Better performance under cyclic loading
- Weldability: Improved joining characteristics
- Thermal Stability: Maintained properties at elevated temperatures
- Chemical Resistance: Enhanced durability in aggressive environments
Latest research indicates that innovations like microalloying and thermomechanical processes are further optimizing seamless pipe applications, making alloys key for manufacturers to comply with the strictest industry standards.
Applications of Seamless Pipes by Industry

Oil and Gas Industry
Seamless pipes are absolutely essential for the oil and gas industry, with applications extending from drilling to production and transportation of hydrocarbons. Their structural reliability is enhanced by the absence of welded seams that could form weak spots.
Key Applications in Oil & Gas:
- Casing: Structural retaining walls of oil and gas wells
- Tubing: Conduit for produced oil and gas from reservoir
- Line Pipes: Transportation of crude oil and natural gas (API 5L grades)
- Drilling: High-pressure drilling operations
- Offshore Platforms: Subsea and offshore production systems
Material Grades: Carbon steel and stainless steel are typical, but duplex and super duplex grades are gaining popularity because of their extraordinary corrosion resistance and mechanical properties. Standards compliance includes API 5L and API 5CT for safety and quality assurance.
Power Generation Applications
Seamless Pipes in Power Plants:
- Boilers: P91 and T22 grades for high-temperature steam generation
- Heat Exchangers: Efficient thermal energy transfer systems
- Steam Lines: High-pressure steam transportation
- Supercritical Systems: Ultra-supercritical power generation with high creep resistance
- Nuclear Reactors: Coolant transport under extreme high-pressure conditions
Automotive Sector
Seamless pipes are major enablers in producing highly precise automotive components. Their high dimensional accuracy and fatigue resistance contribute significantly to vehicle performance and safety.
Automotive Applications:
- Fuel Injection Lines: Precision delivery systems requiring exact dimensions
- Hydraulic Power Systems: High-pressure fluid power transmission
- Structural Parts: Chassis and frame components
- Shock Absorber Systems: Cold-drawn seamless steel tubes for suspension
- Drive Shafts: Power transmission components
- Exhaust Pipes: High-temperature exhaust gas management
- Battery Cooling Systems: Electric vehicle thermal management (emerging application)
Chemical and Petrochemical Processing
Seamless pipes are heavily used in the chemical industry due to their effective resistance against extreme cases of acid, alkali, and other chemicals, allowing safe transportation and storage of chemical materials.
Chemical Industry Requirements
Material Grade: ASTM A312 stainless steel seamless pipes are prevalent due to meeting rigid safety standards.
Applications: Oil refineries, fertilizer production plants, specialty chemical processing units
Benefits: Superior resistance to chemical degradation, safe handling of corrosive substances
Seamless Tubing in Construction and Structural Applications
High-Rise Buildings
Employed in structural frameworks of skyscrapers due to capability to carry enormous loads while offering resistance to external forces like strong winds and earthquakes.
Bridges and Overpasses
Outstanding tensile strength and corrosion resistance play vital roles in bridge construction, providing safety and durability in harsh environmental conditions.
Offshore Platforms
Incorporated in structural parts of offshore drilling platforms, bearing tough marine conditions and heavy operational stresses.
Industrial Sheds & Warehouses
Main components building up industrial structures, supporting large spans while keeping designs lightweight and economical.
Sports Stadiums
Contemporary stadium designs visually combine seamless tubes in roof structures and support systems, achieving both strength and aesthetic appeal.
Foundation Piling
Load-bearing structures and scaffolding with high strength-to-weight ratio and uniform structure for dynamic loads.
Typical Materials: Duplex and carbon steel seamless pipes are selected for their economy and mechanical advantages in construction applications.
Aerospace Industry Reliance on Seamless Pipes
Seamless pipes are a major factor in the aerospace industry since their unique strengths, durability, and precision are impossible to match. These pipes are manufactured as a single piece without a weld seam, giving them the ability to withstand high pressure, extreme temperatures, and mechanical stress.
Aerospace Requirements:
- Lightweight Components: Critical for fuel efficiency and performance
- Corrosion Resistance: Essential for high-altitude environments
- Engine Systems: Meet tough safety and performance standards
- Structural Integrity: Withstand extreme operational conditions
- Precision Manufacturing: Strict dimensional accuracy requirements
Future Trends in Seamless Pipe Manufacturing

Recent analysis shows a growing interest in breakthroughs in seamless pipe manufacturing, mainly concerning performance optimization and sustainability issues. The industry is evolving rapidly with technological innovation and environmental consciousness.
Innovations in Pipe Manufacturing Techniques
Cutting-Edge Technologies:
- 3D Printing/Additive Manufacturing: Production and prototyping of pipes with customized dimensions and properties
- Laser Cutting: Precision cutting with minimal material waste
- Robotics Integration: Amazing level of precision and reduced material waste
- AI-Powered Automation: Optimize production lines and real-time defect identification
- Advanced Materials: High-performance alloys and lightweight composites
- Digital Twins: Virtual modeling for process optimization
Advanced Material Development
| Material Innovation | Characteristics | Target Applications |
|---|---|---|
| Titanium Alloys | Enhanced strength-to-weight ratio | Aerospace applications requiring mass reduction |
| Advanced Composites | Lightweight, high-strength materials | Special-purpose applications |
| High-Performance Alloys | Superior mechanical properties | Extreme environment applications |
| Nano-Enhanced Materials | Improved structural characteristics | Next-generation engineering |
Sustainability Practices in Seamless Pipe Production
Sustainability in seamless pipe production has taken a giant leap forward thanks to the adoption of energy-efficient techniques and innovative production methods.
Circular Economy Principles
Steel scrap recycling and raw materials recycling leading to major decline in environmental footprint of production process.
Energy Management Systems
Optimized thermal and mechanical processes cutting down fossil fuel use and reducing greenhouse gas emissions.
Carbon Capture Technology
Top-notch technologies to reduce emissions from industrial operations and improve environmental performance.
Waste Heat Recovery
Capturing and reusing waste heat from production processes to improve overall energy efficiency.
Smart Manufacturing
AI-driven systems ensuring most efficient resource use and least waste generation through real-time monitoring.
Clean Production Technologies
Inductive heating and hydro-forming techniques cutting down power use while preserving material characteristics.
Environmental Focus: All these practices reflect that the seamless pipe industry is in tune with modern-day sustainability standards, not only making the world better but also keeping up with contemporary times and solving environmental issues on a global scale.
Market Outlook for Seamless Pipe Manufacturing
The forecasts for seamless pipe production indicate vigorous growth, and this is the consequence of both industrial need and tech improvement. Seamless pipes are indispensable across multiple industries where durability, corrosion resistance, and high-pressure capability are essential.
📊 Market Growth Drivers:
- Infrastructure development in Asia-Pacific and Middle East
- Global energy transition requiring clean fuel transportation
- Increased safety standards in alternative energy applications
- Growing demand for higher-grade seamless steel pipes
- Renewable energy sector expansion
Future Growth Areas:
- Renewable Energy: Offshore wind farms, solar thermal systems
- Hydrogen Infrastructure: Clean fuel transportation and storage
- Carbon Capture Systems: Environmental technology applications
- Advanced Manufacturing: Industry 4.0 integration
- Smart Cities: Modern infrastructure requirements
Ten-Year Outlook: Strong market resistance and wide prospects of growth with focus on environmentally friendly production practices and adaptation to clean energy requirements.
Industry Standards and Compliance
Seamless pipes must comply with rigorous industry standards to ensure safety, quality, and performance across all applications.
| Standard Organization | Key Standards | Application Focus |
|---|---|---|
| ASTM International | A106, A53, A335, A312, A333 | Material specifications, testing methods, mechanical properties |
| API (American Petroleum Institute) | API 5L, API 5CT | Oil and gas pipelines, casing, and tubing specifications |
| ASME | ASME B31.1, B31.3, B31.4, B31.8 | Piping systems, pressure vessels, power piping |
| ISO Standards | ISO 9001, ISO 14001 | Quality management, environmental management systems |
| DIN Standards | Various European specifications | International manufacturing requirements |
References
-
Online Eccentricity Monitoring of Seamless Tubes (University of Michigan)
This document discusses quality inspection methods, such as ultrasonic testing, used in seamless tube manufacturing plants.
Read more here -
Steel Tube and Pipe Manufacturing Processes (Academia.edu)
This paper provides a comprehensive overview of various manufacturing processes for seamless steel tubes and pipes.
Read more here -
Michigan Seamless Tube Company Report (University of Michigan)
This report includes detailed data on seamless tube properties, stress testing, and manufacturing standards.
Read more here
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is meant by seamless tube and pipe manufacturing?
Seamless tube and pipe manufacturing is a process to make tubes and pipes that are free from welding seams resulting in a strong, and good quality product. A solid round billet is the primary material for this technique and it goes through a number of steps like piercing, elongation, and rolling to get the appropriate size and thickness of the walls.
What advantages does seamless steel pipe have over welded types?
Seamless steel pipe is stronger, able to withstand pressure better, and does not contain weak areas like welded pipes that may lead to leakage. Besides, seamless tubes pipes are less prone to breakage under extremely difficult situations, hence they can be used in high-stress applications such as hydraulic cylinders and oil-gas exploration.
How does one decide on the diameter and wall thickness of seamless pipes?
Pipes’ diameter and wall thickness are decided according to their application needs. Manufacturers can make pipes of different sizes, from small to large, thus ensuring that the wall thickness meets the required standards for strength and durability throughout.
What are the steps in seamless tube production?
Seamless tube production usually consists of several important operations: piercing a round bar to make a hollow shell, then elongating, rolling in a mill, and heat treatment through annealing or reheat treatment. All these processes are carried out to ensure that the finished product has the required quality and performance specifications.
Is it possible to cold draw seamless tubes, and what are the advantages?
Definitely, seamless tubes can be cold drawn, which means that the diameter is reduced, and at the same time, the length of the pipe is achieved at room temperature. The cold drawing process not only enhances surface quality but also provides more accurate dimensions of diameter and wall thickness, and increases the mechanical properties making the tubes usable for precision applications.
What significance does heat treatment carry in seamless tube manufacturing?
Heat treatment is very important in the manufacturing of seamless tubes since it can improve the metal’s mechanical characteristics. Annealing and reheat treatment to aid in stress relieving, ductility increase, and ultimately imparting the strength and toughness needed for that application are processes that the final product undergoes.
What technologies are mainly used in making seamless pipes?
The leading methods of producing seamless pipes are mandrel rolling, pilger rolling, and extrusion. Each of them has pros and cons, but the one chosen will depend on the size, wall thickness, and application of the finished product, among other things.
Where are seamless pipes commonly used?
Because of their strength and reliability, seamless pipes have an extensive range of applications in different industries. The main sectors are construction, automotive, oil and gas transportation, as well as hydraulic cylinder manufacturing. Their high-pressure and high-temperature resistance makes them suitable for critical applications and thus preferred over other types.
How is pipe length determined during manufacturing?
Pipe length is determined by the manufacturer according to customer and application requirements during the manufacturing process. The manufacturer is capable of producing seamless pipes of different lengths thus catering to various industries requirements and at the same time making sure that the pipes meet the performance and durability standards.







