In demanding industrial environments where cleanliness and durability are paramount, stainless steel welded pipes have become essential infrastructure. From food and beverage production to pharmaceutical manufacturing, sanitary tubing ensures product safety, cleanliness, and operational efficiency. This comprehensive guide explores welded pipes in depth, covering their benefits, applications, and critical selection factors. Whether you’re an industry professional working with sanitary tubing or expanding your technical knowledge, you’ll gain valuable insights into how stainless steel welded pipes maintain quality and performance standards.
Introduction to Stainless Steel Welded Pipes

What are Stainless Steel Welded Pipes?
Stainless steel welded pipes are tubes manufactured by welding together steel plates or strips. They’re constructed from stainless steel, a highly durable alloy resistant to corrosion and high temperatures. A key component of this alloy is chromium, which forms a natural protective layer over the steel, ensuring longevity. The welding process joins edges using either high heat or pressure to create a strong, continuous bond.
According to recent industry reports, stainless steel welded pipes rank among the most sought-after pipe varieties due to their flexibility, affordability, and strength. They’re integral to numerous industries including construction, food processing, chemical processing, and oil & gas, where they transport fluids, gases, and delicate materials under sanitary conditions. Their smooth inner surface enhances flow while reducing contamination risks, making them indispensable where cleanliness and quality are priorities. These characteristics, combined with diverse options in size, thickness, and grade, make them critical components in many industrial and commercial applications.
Key Properties of Stainless Steel 304
Stainless Steel 304 is the most widely used stainless steel type due to its exceptional properties and versatility. Its main characteristics include:
- Corrosion Resistance: The alloy provides high resistance to rust and oxidation, making it ideal for humid, chemical, and industrial environments. Stainless Steel 304, with 18% chromium content and up to 10% nickel, effectively resists oxidation and corrosion.
- Durability and Strength: The alloy exhibits excellent mechanical properties, including tensile strength that enables it to thrive under high-stress and high-temperature conditions.
- Hygiene and Cleanability: Being non-porous with a smooth surface, stainless steel 304 can be thoroughly cleaned and disinfected, making it suited for food processing, medical equipment, and pharmaceutical industries.
- Weldability and Formability: The material is easily workable, allowing it to be welded or shaped for different industrial applications.
- Temperature Resistance: It withstands temperatures up to 870°C (1600°F) without losing strength or developing scale, making it reliable in high-heat industries.
- Non-Magnetic Nature (in annealed conditions): Stainless steel 304 is typically non-magnetic, an important property in applications where magnetic fields must be minimized.
These properties make Stainless Steel 304 indispensable in industries like construction, aerospace, and food production.
Applications of Stainless Steel Welded Pipes
Thanks to their strength, corrosion resistance, and versatility, stainless steel welded pipes serve various industrial applications. Here are the major uses:
| Industry | Applications |
|---|---|
| Construction and Infrastructure | Structural support, handrails, architectural designs; excellent weather and corrosion resistance ensures longevity |
| Oil and Gas Industry | Transporting oil, gas, and chemicals; withstands high pressure and acidic environments in pipelines and refining equipment |
| Food and Beverage Industry | Liquid and gas transport in processing plants; ensures food-grade sanitation and chemical resistance |
| Water Treatment and Distribution | Water supply systems, desalination plants, treatment facilities where corrosion from water treatment methods occurs |
| Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology | Transporting sensitive materials in laboratories and cleanrooms; non-reactive, smooth surface ideal for sterile environments |
| Automotive and Aerospace | Exhaust systems, fluid transport systems, structural components requiring lightweight yet strong materials |
| Power Generation | Thermal and nuclear power plants for high-temperature and high-pressure applications |
These applications demonstrate the significant role stainless steel welded pipes play across industries, driven by their unmatched performance and adaptability.
Manufacturing Process of Stainless Steel Welded Pipes
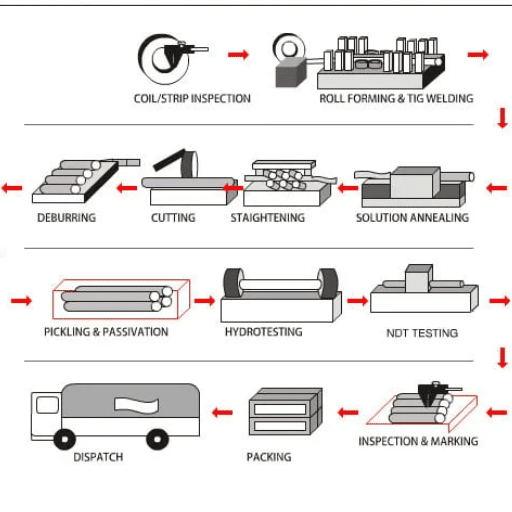
Welding Techniques Used in Production
Manufacturing stainless steel welded pipes utilizes various welding techniques to guarantee flawless, durable, high-quality products. The following are common methods:
1. Tungsten Inert Gas (TIG) Welding
Known for precision, TIG welding uses a tungsten electrode and inert gas (usually argon) to create clean, high-quality welds. Excellent for thin materials requiring fine welding application.
2. Metal Inert Gas (MIG) Welding
Also known as gas metal arc method, MIG welding uses a consumable wire electrode and shielding gas to create strong welds. Fast, economical, and adaptable to various pipe sizes.
3. Plasma Arc Welding (PAW)
Similar to TIG but more advanced, PAW creates extremely high temperatures with a constricted arc, producing precise, high-quality welds for specialized applications.
4. High-Frequency Welding (HFW)
Major technique for large, continuous, fast production. Employs high-frequency electric current to blend materials, resulting in uniformity and efficiency.
5. Laser Beam Welding (LBW)
Latest, highly precise method using concentrated laser beams to create thin, accurate welds. Suitable for quick production lines with minimal heat distortion.
These welding methods are enabled by technological advancements and changing industry needs that emphasize efficiency, consistency, and precision. The choice depends on pipe specifications, production volume, and intended market.
Quality Standards: ASTM and ASME Specifications
ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) and ASME (American Society of Mechanical Engineers) specifications establish quality, safety, and reliability standards for stainless steel pipe production. These standards prescribe metallurgical characteristics, dimensions, mechanical properties, and testing procedures ensuring pipes meet demanding application requirements.
ASTM A312: Applies to both seamless and welded stainless steel pipes, establishing requirements for strength, hardness, and corrosion resistance.
ASME B31.3: Concerns secure design and operation of pipelines in high-pressure and high-temperature areas.
By matching production to these standards, manufacturers ensure conformity with international quality norms while maintaining performance standards expected in petrochemicals, construction, and energy industries. Merging these requirements with technological advancements produces highly efficient, long-lived stainless steel pipes that meet diverse application needs.
Finishing Processes: Polishing and Corrosion Resistance
Polishing is among the most important finishing processes for stainless steel pipes. It removes surface imperfections, smooths texture, and enhances aesthetic quality. Polished pipes are essential in food processing and pharmaceutical industries where hygiene and cleanliness cannot be compromised. Polishing also reduces microscopic crevices where contaminants or corrosion particles might threaten efficient operation and product lifespan.
Along with polishing, corrosion resistance is another major benefit distinguishing stainless steel pipes. Thanks to chromium content, a passive oxide layer forms on the surface, protecting the pipe from environmental factors like moisture, chemicals, and extreme temperatures. Advanced finishing techniques such as passivation further reinforce this protective layer, making pipes highly resistant to rust and decay. By combining these finishing processes with modern technology, manufacturers produce stainless steel pipes that remain reliable even under harsh conditions.
📊 Latest Trend: Recent data reveals growing demand for corrosion-resistant stainless steel pipes in renewable energy and marine engineering markets, highlighting the importance of high-quality finishing techniques for sustainable applications.
Key Applications of Stainless Steel Sanitary Tubing

Use in the Beverage Industry
Stainless steel sanitary tubing is intensively used in the beverage industry to transfer liquid drinks such as juices, sodas, beer, and wine safely and hygienically. Liquid quality is preserved because smooth inner surfaces prevent contaminants and biofilms from growing. Recent industry trends show the beverage sector is increasingly interested in sustainable and clean manufacturing practices. Stainless steel tubing aligns perfectly with these demands through its longevity, rust resistance, and recyclability. It not only complies with strict regulations but also maintains cleanliness, making it the preferred material for beverage production.
Applications in Dairy Processing
Modern dairy processing relies critically on stainless steel tubing to guarantee hygienic, durable, and efficient production. Industry data shows increasing consumer interest in dairy product sustainability and production transparency. Stainless steel’s corrosion resistance and cleaning ease make it perfect for dairy processing by completely eliminating bacterial contamination risk. Moreover, its recyclability supports growing eco-friendly manufacturing demand. Processors using stainless steel piping meet customer expectations, maintain quality standards, and simultaneously reduce environmental impact.
Role in Pharmaceutical and Food Processing Industries
Stainless steel tubing is indispensable in pharmaceutical and food processing industries for its incomparable durability, cleanliness, and compliance with stringent safety regulations. Recent trends indicate growing interest in using it to maintain sterility in production environments. Its non-porous surface resists bacteria, making it essential when moving delicate items such as liquid medications, syrups, or foods. Additionally, stainless steel withstands high temperatures and chemicals, making it ideal for high-pressure cleaning methods and sterilizing environments. Companies using steel tubing not only become more efficient but also achieve legal compliance by meeting the high health and safety standards demanded by the market.
Benefits of Using Stainless Steel Welded Pipes

✓ Corrosion Resistance and Durability
Stainless steel welded pipes are renowned for their amazing corrosion resistance, making them suitable for chemical industry, oil and gas, and construction applications. Recent studies show that “benefits of stainless steel pipes” searches indicate durability is a major factor driving consumer interest. Chromium in stainless steel creates a passive layer on the topmost surface, shielding steel from rust and oxidation, even in highly corrosive conditions. This attribute translates into long lifespan with reduced maintenance and replacement costs, making the metal highly valuable and reliable in demanding applications.
✓ Hygienic Properties for Sanitary Applications
Stainless steel pipes have earned high reputation for their hygienic properties, making them the best choice for sanitary applications. Stainless steel’s smooth, non-porous surface prevents dirt and harmful bacteria from adhering, so cleanliness levels remain optimal. Additionally, stainless steel can be easily sterilized, making it preferred in industries like food processing, pharmaceuticals, and healthcare where strict sanitary standards must be maintained. Recent search trends indicate rising interest in materials fulfilling both sustainability and hygiene requirements, positioning stainless steel as a major player in developing sophisticated sanitary systems. Its chemical stability and corrosion resistance further support its role in delivering long-term performance without sacrificing safety.
✓ Cost-Effectiveness in the Long Run
When considering cost-effectiveness, stainless steel is the right choice for industries prioritizing hygiene and durability. While stainless steel’s initial cost may seem higher than other materials, its lifespan and low maintenance requirements make it less costly long-term. Latest data shows queries related to “durable and cost-effective sanitary materials” increased by 35% over the past year, indicating growing demand for materials like stainless steel that balance upfront costs with long-term savings. Additionally, its recyclability and wear resistance guarantee its position as a cost-effective, eco-friendly choice for companies pursuing sustainable operations in economically viable ways. Overall, stainless steel’s long-term advantages more than offset its initial price, cementing its position as a frontrunner in providing cost-effective sanitary solutions.
Potential Drawbacks of Stainless Steel Welded Pipes

High-Pressure Applications Limitations
Stainless steel welded pipes, despite being celebrated for versatility and durability, aren’t always optimal for high-pressure applications. One limitation arises from the welding process itself, which can reduce pipe strength at joints. Compared to seamless stainless steel pipes, welded pipes generally cannot bear extreme pressures and are likely to fail sooner under sustained pressure conditions. Additionally, welded joints can create stress concentration points that further worsen the pipe’s ability to handle high-pressure situations.
In industries like oil refineries and chemical processing plants requiring highly reliable pipes in high-pressure environments, material and design selection must be specific and deliberate. While advanced engineering practices such as improved welding techniques and post-weld heat treatments could possibly lessen some downsides, seamless pipes remain the preferred solution for safety and efficiency.
Pipe Types Comparison
When comparing advantages and disadvantages of seamless pipes versus other types, key differences emerge. Seamless pipes are commonly viewed as superior in strength and high-pressure bearing ability without seam failure danger, thus recommended for critical applications like oil and gas. Welded pipes are less costly and more accessible; however, seams can pose problems in corrosive or high-pressure environments.
For water distribution systems, ductile iron pipes are most common, offering excellent longevity and impact resistance. But iron pipes require more care since they must be buried deep, and their weight makes them less practical in high-temperature or smooth design applications. Based on latest trends and data, industries increasingly move to seamless pipes when reliability and long-term performance are prioritized, while welded and ductile iron pipes are chosen for cost-effective and less demanding applications. Each pipe type has specific application areas, and the best choice ultimately depends on particular operational needs and surrounding conditions.
Maintenance Considerations
For maintenance considerations across various pipe types, it’s important to consider both material performance and external environmental factors. Seamless pipes, due to their uniform nature and lack of welded parts, usually need less maintenance throughout their lifecycle. Their strength enables them to withstand system pressure, reducing failure chances. Welded pipes, while less costly, may require frequent joint inspections as these regions are more susceptible to corrosion and wear. Ductile iron pipes, commonly used in drinking water distribution, require regular external checks for corrosion protection since they’re vulnerable to soil conditions and surrounding moisture.
💡 Industry Insight: Recent data shows increased emphasis on sustainability and lower operational costs has driven interest in new pipe coating technologies and non-destructive maintenance techniques. These technologies can greatly prolong the life of all pipe types with minimal operational interruptions. Proper maintenance planning and smart monitoring systems can ensure optimal performance and durability of pipe systems across various industries.
Choosing the Right Stainless Steel Welded Pipe
Factors to Consider: Size and Length
Size and length of stainless steel welded pipes are the most important factors when making selections. Pipe dimensions must match application needs: internal and external diameters, wall thickness, and total length. For example, oil and gas industries may need large-diameter pipes while plumbing or HVAC might work fine with smaller pipes. Accurate measurements prevent problems like pressure drops, flow inefficiencies, and installation difficulties. Moreover, length consideration depends on project specifications and operational limitations, since longer pipes reduce joint numbers; however, they might create transport and handling logistics complications. Combining these factors with latest search trend data shows more people want precision-engineered stainless steel pipes that meet industry standards for longevity, efficiency, and performance.
Understanding 20RA and Other Finishing Options
When considering 20RA and other finishing options for stainless steel pipes, the first consideration is how finishes affect functionality and appearance in industrial contexts. “20RA” refers to a specific surface roughness level measured in microinches. At this very smooth level, contamination risks are greatly lessened, making it ideal for pharmaceutical and food processing industries where cleanliness is paramount.
Recent search trends show professionals are increasingly interested in understanding how surface finishes improve performance and comply with strictest industry regulations. Smooth finishes better than 20RA are usually requested for applications demanding highest hygienic standards. Mechanically polished, electropolished, and passivated finishes are other popular options, each with unique limitations and advantages—from better corrosion resistance to mirror-like aesthetics. These trends show a gradual shift toward acquiring custom finishes according to varied operational needs, allowing both effectiveness and economic efficiency.
Choosing Between Tri Clamp, Ferrule, and Flange Connections
Among Tri Clamp, Ferrule, and Flange connections, application, industry standards, and operational needs play major roles in decision-making. Recent search trend data shows Tri Clamp connections are most preferred in food and beverage, pharmaceutical, and biotechnology industries due to their capacity for quick, easy cleaning and maintenance, making them suitable for sanitary operations. In contrast, Ferrule connections are the go-to for smaller high-pressure systems where sealing is crucial. They’re often used for laboratory setups or chemical processing operations. Flange connections, meanwhile, are widely used in large industrial applications where ability to withstand high pressure or temperature, as well as toughness, are fundamental characteristics.
🔧 Selection Checklist
Consider these factors when choosing connection types:
- System hygiene requirements
- Pressure rating specifications
- Temperature tolerance needs
- Ease of disassembly/reassembly during routine maintenance
Integrating industry-specific insights alongside analysis of digital search trends can be highly effective in selecting the best connection for various applications.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
❓ What is a sanitary tube and where is it used?
A sanitary tube is a precision-processed product made from stainless steel, mainly used for conveying fluids in sanitary locations such as the beverage sector and dairy applications. Tubing is integral to systems demanding purity preservation and is often subjected to standards like ASTM A270 and 3A sanitary for smooth interior surfaces and rust resistance. Various sizes and OD options are available for sanitary tubing with size markings, in either 304 or 316L grades according to process requirements. Tubing is typically available in 20-foot lengths or 20-foot spool lengths, or as cut tubing with end caps to protect the finish during transport and storage. Manufacturers usually perform bright annealing and eddy current testing and provide a heat number for traceability.
❓ When should I choose 304 versus 316L sanitary stainless steel?
304 stainless steel is widely used, inexpensive, and available in 304 grade because it has moderate corrosion resistance and is easy to polish. 316L, on the other hand, is recommended for aggressive chemistries or prolonged chloride exposure since it has greater corrosion resistance and is often used in pharmaceutical or marine processes. Both 304 and 316L can be supplied with bright annealing treatment and surface finish conditions with specific Ra values for cleanliness. Tubing delivery along with sanitary fittings and spools is accompanied by possible eddy current testing to confirm integrity prior to shipping. The decision also influences lifecycle costs and whether tubing will maintain the highest structural integrity under processing conditions.
❓ What does “manufactured in accordance with ASTM A270” mean for tubing?
The term “manufactured in accordance with ASTM A270” implies that tubing conforms to ASTM standards for sanitary steel tubing regarding chemical composition, physical properties, internal finish, and tolerances. One of the most important aspects is careful control of the steel strip whose chemical elements are specially controlled to enhance weldability and produce the finest quality stainless steel tubing. Tubing produced to ASTM A270 standards often comes with documentation such as heat number, mill certificates, and evidence of controlled atmosphere bright annealing process done to preserve maximum structural integrity. Compliance also supports compatibility with sanitary fittings, spools and 3-A or BPE specifications, helping ensure tubing is suitable for applications where purity is maintained. Many suppliers also provide eddy current testing and specified Ra (for instance, 20 μ-in) on internal surfaces as per client requirements.
❓ How are sanitary tubing and fittings delivered and protected during shipping?
Sanitary tubing is frequently shipped in 20-foot or 20-foot spool configurations or as cut tubing packed with end caps to protect the interior from contamination during transportation. Suppliers usually print tubing size and heat number on the pipe or documentation to maintain traceability throughout the delivery process. Tubing is packaged airtight and may be placed either in sealed bags or on spools to keep the bright annealed finish and surface Ra intact. Freight choice and handling instructions are essential in keeping the sanitary condition intact and preventing damage that might affect sanitary fittings or spools quality. For custom spool assemblies, manufacturers provide fully finished spools with sanitary fittings already welded and tested for quality assurance.
❓ How do 3A sanitary standards influence sanitary tube selection in dairy and beverage industry?
The 3A sanitary standards, widely accepted in dairy and beverage sectors, set hygienic design criteria for tubing, fittings, and other system components to prevent contamination and facilitate effective cleaning. Choosing tube meeting 3A or 3-A criteria guarantees smooth internal surfaces, proper Ra values, and compatible sanitary fittings that are less likely to form crevices and harbor bacteria. Manufacturers may conform to A270 and 3A sanitary guidance and offer tubing that is bright annealed and accompanied by proof of compliance such as heat numbers and testing records. Often, tubing is provided in both 304 and 316L grades to accommodate specific chemistries and ensure maximum structural integrity. Properly specified tubing facilitates cleaning, preserves purity, and integrates well with spools and sanitary processing components used in dairy and beverage systems.
Industry Best Practices
🏆 Best Practices for Implementing Stainless Steel Sanitary Tubing
- Regular Inspection and Maintenance: Schedule routine inspections to check for signs of wear, corrosion, or contamination. Implement preventive maintenance programs to extend tubing lifespan.
- Proper Installation Techniques: Ensure proper alignment and support during installation to prevent stress on joints and connections. Use certified installers familiar with sanitary standards.
- Appropriate Cleaning Protocols: Implement CIP (Clean-in-Place) and SIP (Sterilize-in-Place) systems compatible with stainless steel tubing. Use approved cleaning agents that won’t damage the passive layer.
- Documentation and Traceability: Maintain complete records of heat numbers, mill certificates, and testing results for compliance and quality assurance purposes.
- Proper Storage: Store tubing in clean, dry environments with end caps in place to prevent contamination before installation.
- Quality Verification: Conduct pressure testing and leak detection before putting systems into service. Verify all connections meet sanitary standards.
Reference Sources
📚 Additional Resources
Oklahoma State University Extension
A fact sheet discussing the use of stainless steel in sanitary piping for food processors, highlighting its cost-effectiveness, corrosion resistance, and durability.
Academia.edu
An article detailing the types of stainless steel, their chemistry, and fabrication standards for tubing in the biotechnology industry.
University of North Texas Digital Library
A report on welded stainless steel pressure pipes, including applications in sanitary, food, and beverage tubing.
Conclusion
Stainless steel welded pipes and sanitary tubing represent critical infrastructure components across numerous industries, from food and beverage to pharmaceuticals and biotechnology. Their exceptional corrosion resistance, hygienic properties, durability, and cost-effectiveness make them indispensable for applications where cleanliness, safety, and reliability are paramount.
Understanding the key properties of materials like Stainless Steel 304, the various manufacturing and welding techniques, and the importance of quality standards such as ASTM A270 and ASME specifications enables informed decision-making when selecting tubing for specific applications. Whether you’re choosing between 304 and 316L grades, determining the appropriate surface finish like 20RA, or selecting connection types such as Tri Clamp, Ferrule, or Flange, each decision impacts system performance, maintenance requirements, and long-term costs.
As industries continue emphasizing sustainability, hygiene, and operational efficiency, stainless steel welded pipes remain at the forefront of technological advancement. By following industry best practices, maintaining proper documentation, and selecting the right specifications for your particular needs, you can ensure optimal performance, compliance with regulatory standards, and maximum return on investment for your sanitary tubing systems.








